Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L Software Guide - Page 132
DHCP Client Request Process, DHCP Request for IP Information from a DHCP Server
 |
View all Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 132 highlights
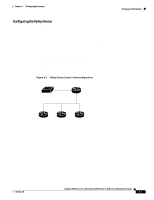
Changing IP Information Chapter 6 Configuring the System DHCP Client Request Process When you boot your switch, the DHCP client can be invoked and automatically request configuration information from a DHCP server under these conditions: • The configuration file is not present on the switch. • The configuration file is present, but the IP address is not specified in it. • The configuration file is present, the IP address is not specified in it, and the service config global configuration command is included. This command enables the autoloading of a configuration file from a network server. Figure 6-1 shows the sequence of messages that are exchanged between the DHCP client and the DHCP server. Figure 6-1 DHCP Request for IP Information from a DHCP Server Switch A DHCPDISCOVER (broadcast) DHCPOFFER (unicast) DHCPREQUEST (broadcast) DHCPACK (unicast) DHCP server 47570 The client, Switch A, broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to locate a DHCP server. The DHCP server offers configuration parameters (such as an IP address, subnet mask, gateway IP address, DNS IP address, a lease for the IP address, and so forth) to the client in a DHCPOFFER unicast message. In a DHCPREQUEST broadcast message, the client returns a request for the offered configuration information to the DHCP server. The request is broadcast so that all other DHCP servers that received the DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message from the client can reclaim the IP addresses that they offered to the client. The DHCP server confirms that the IP address has been allocated to the client by returning a DHCPACK unicast message to the client. With this message, the client and server are bound, and the client uses configuration information received from the server. The amount of information the switch receives depends on how you configure the DHCP server. For more information, see the "Configuring the DHCP Server" section on page 6-5. If the configuration parameters sent to the client in the DHCPOFFER unicast message by the DHCP server are invalid (a configuration error exists), the client returns a DHCPDECLINE broadcast message to the DHCP server. The DHCP server sends the client a DHCPNAK denial broadcast message, which means the offered configuration parameters have not been assigned, an error has occurred during the negotiation of the parameters, or the client has been slow in responding to the DHCPOFFER message (the DHCP server assigned the parameters to another client) of the DHCP server. A DHCP client might receive offers from multiple DHCP or BOOTP servers and can accept any one of the offers; however, the client usually accepts the first offer it receives. The offer from the DHCP server is not a guarantee that the IP address will be allocated to the client; however, the server usually reserves the address until the client has had a chance to formally request the address. If the switch accepts replies from a BOOTP server and configures itself, the switch will broadcast, instead of unicast, TFTP requests to obtain the switch configuration file. Catalyst 2900 Series XL and Catalyst 3500 Series XL Software Configuration Guide 6-4 78-6511-08