Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L Software Guide - Page 174
Configuring STP Root Guard
 |
View all Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 174 highlights
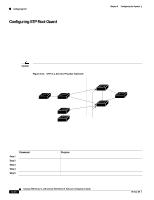
Configuring STP Chapter 6 Configuring the System Configuring STP Root Guard The Layer 2 network of a service provider (SP) can include many connections to switches that are not owned by the SP. In such a topology, STP can reconfigure itself and select a customer switch as the STP root switch, as shown in Figure 6-11. You can avoid this situation by configuring the root-guard feature on interfaces that connect to switches outside of your customer's network. If STP calculations cause an interface in the customer network to be selected as the root port, root guard then places the interface into the root-inconsistent (blocked) state to prevent the customer switch from becoming the root switch or being in the path to the root. If a switch outside the network becomes the root switch, the interface is blocked (root-inconsistent state), and STP selects a new root switch. The customer switch does not become the root switch and is not in the path to the root. Caution Misuse of this feature can cause a loss of connectivity. Figure 6-11 STP in a Service Provider Network Customer network Potential spanning-tree root without root guard enabled Service-provider network Desired root switch 43578 Enable the root-guard feature on these interfaces to prevent switches in the customer network from becoming the root switch or being in the path to the root. Root guard enabled on a port applies to all the VLANs that the port belongs to. Each VLAN has its own instance of STP. Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to set root guard on a port: Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Command configure terminal interface interface spanning-tree rootguard end show running-config Purpose Enter global configuration mode. Enter interface configuration mode, and enter the port to be configured. Enable root guard on the port. Return to privileged EXEC mode. Verify that the port is configured for root guard. Use the no version of the spanning-tree rootguard command to disable the root guard feature. 6-46 Catalyst 2900 Series XL and Catalyst 3500 Series XL Software Configuration Guide 78-6511-08