Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L Software Guide - Page 166
CSUF implements the Stack Membership Discovery Protocol and the Fast Uplink Transition Protocol.
 |
View all Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 166 highlights
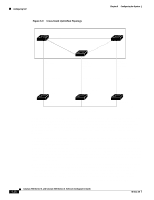
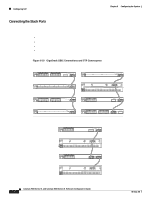
Configuring STP Figure 6-9 Cross-Stack UplinkFast Topology Spanning tree root Fwd Backbone Fwd Fwd Chapter 6 Configuring the System Link A (Root link) 100 or 1000 Mbps Link B (Alternate redundant link) 100 or 1000 Mbps Link C (Alternate redundant link) 100 or 1000 Mbps Stack root port Alternate stack root port Alternate stack root port Switch A Stack port Switch B Stack port Switch C Stack port 47572 Multidrop backbone (GigaStack GBIC connections) CSUF implements the Stack Membership Discovery Protocol and the Fast Uplink Transition Protocol. Using the Stack Membership Discovery Protocol, all stack switches build a neighbor list of stack members through the receipt of discovery hello packets. When certain link loss or STP events occur (described in the "Events that Cause Fast Convergence" section on page 6-39), the Fast Uplink Transition Protocol uses the neighbor list to send fast-transition requests on the stack port to stack members. The switch sending the fast-transition request needs to do a fast transition to the forwarding state of a port that it has chosen as the root port, and it must obtain an acknowledgement from each stack switch before performing the fast transition. Each switch in the stack determines if the sending switch is a better choice than itself to be the stack root of this STP instance by comparing STP root, cost, and bridge ID. If the sending switch is the best choice as the stack root, the switch in the stack returns an acknowledgement; otherwise, it does not respond to the sending switch (drops the packet) and prevents the sending switch from receiving acknowledgements from all stack switches. When acknowledgements are received from all stack switches, the Fast Uplink Transition Protocol on the sending switch immediately transitions its alternate stack root port to the forwarding state. If acknowledgements from all stack switches are not obtained by the sending switch, the normal STP transitions (blocking, listening, learning, forwarding) take place, and the spanning-tree topology converges at its normal rate (2 * forward-delay time + max-age time). The Fast Uplink Transition Protocol is implemented on a per-VLAN basis and affects only one STP instance at a time. 6-38 Catalyst 2900 Series XL and Catalyst 3500 Series XL Software Configuration Guide 78-6511-08