Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L Software Guide - Page 252
Changing the Pruning-Eligible List, Configuring the Native VLAN for Untagged Traffic
 |
View all Cisco WS-C2960S-24PD-L manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 252 highlights
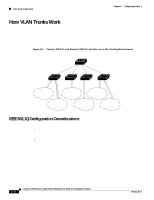
How VLAN Trunks Work Chapter 8 Configuring VLANs Changing the Pruning-Eligible List The pruning-eligible list applies only to trunk ports. Each trunk port has its own eligibility list. VTP Pruning must be enabled for this procedure to take effect. The "Enabling VTP Pruning" section on page 8-19 describes how to enable VTP pruning. Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to remove VLANs from the pruning-eligible list on a trunk port: Step 1 Step 2 Command configure terminal interface interface-id Step 3 switchport trunk pruning vlan remove vlan-id Step 4 Step 5 exit show interface interface-id switchport Purpose Enter global configuration mode. Enter interface configuration mode, and select the trunk port for which VLANs should be pruned. Enter the VLANs to be removed from the pruning-eligible list. Separate nonconsecutive VLAN IDs with a comma and no spaces; use a hyphen to designate a range of IDs. Valid IDs are from 2 to 1001. VLANs that are pruning-ineligible receive flooded traffic. Return to privileged EXEC mode. Verify your settings. Configuring the Native VLAN for Untagged Traffic A trunk port configured with 802.1Q tagging can receive both tagged and untagged traffic. By default, the switch forwards untagged traffic with the native VLAN configured for the port. The native VLAN is VLAN 1 by default. For information about 802.1Q configuration issues, see the "IEEE 802.1Q Configuration Considerations" section on page 8-26. Note The native VLAN can be assigned any VLAN ID, and it is not dependent on the management VLAN. Beginning in privileged EXEC mode, follow these steps to configure the native VLAN on an 802.1Q trunk: Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Command Purpose configure terminal Enter global configuration mode. interface interface-id Enter interface configuration mode, and define the interface that is configured as the 802.1Q trunk. switchport trunk native vlan vlan-id Configure the VLAN that is sending and receiving untagged traffic on the trunk port. Valid IDs are from 1 to 1001. show interface interface-id switchport Verify your settings. If a packet has a VLAN ID that is the same as the outgoing port native VLAN ID, the packet is sent untagged; otherwise, the switch sends the packet with a tag. 8-30 Catalyst 2900 Series XL and Catalyst 3500 Series XL Software Configuration Guide 78-6511-08