Compaq nx9010 Maintenance and Service Guide - Page 114
Power-On Self-Test, Table 3-4. POST Terminal-Error Beep Codes, Beep Codes, POST Description - chipset
 |
View all Compaq nx9010 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 114 highlights
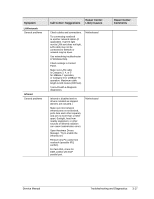
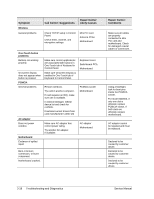
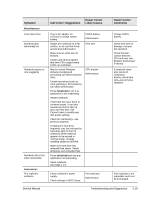
Power-On Self-Test NOTE: If Quiet Boot is enabled in BIOS Setup (the default setting), press esc during boot to see POST messages. When the notebook boots, its system BIOS runs a series of initialization routines and diagnostic tests called POST (Power-On Self-Test). The BIOS will not boot the notebook's operating system if the system memory, CPU, DMA, or interrupt controller fails the POST diagnostic tests. POST indicates progress by a sequence of codes; if an error occurs, the BIOS displays a message and/or issues a beep code. Note that not all POST messages indicate a failure in the notebook-some messages are for information only. You should not necessarily interpret the failure of one or more POST tests as a hardware, software, or firmware failure. If POST displays an error message or issues a beep code indicating an error, confirm the problem using other diagnostic tools. First, confirm the failure by performing a "clean" boot, as described below. Note that if the notebook fails to restart with a clean boot, it requires repair. 1. Remove all accessories, including SDRAM modules, port replicator, PC cards, printer, external monitor, pointing device, and keyboard. 2. Provide "clean" AC power-no auto adapter or unusual AC adapter configuration. 3. Press the reset button to return the notebook to a known state. 4. Press the power button to start the notebook. If the BIOS detects a terminal error condition, it halts POST after issuing a beep code and/or displaying a message (see the following table). The beep code indicates the POST routine in which the terminal error occurred. Beep Codes 1 1-2 1-1-1-3 1-1-1-4 1-1-2-1 1-1-2-3 1-1-2-4 1-1-3-1 1-1-3-2 1-1-3-3 1-1-3-4 1-1-4-1 1-1-4-3 1-1-4-4 1-2-1-1 Table 3-4. POST Terminal-Error Beep Codes POST Description One short beep before boot Search for option ROMs Verify Real Mode Disable Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI) Get CPU type Initialize system hardware Disable shadow and execute code from ROM Initialize chipset with initial POST values Set IN POST flag Initialize CPU registers Enable CPU cache Initialize caches to initial POST values Initialize I/O component Initialize local bus IDE Initialize Power Management 3-22 Troubleshooting and Diagnostics Service Manual