Netgear GS748Tv5 Software Administration Manual - Page 172
IPv6 Class Configuration
 |
View all Netgear GS748Tv5 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 172 highlights
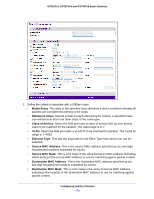
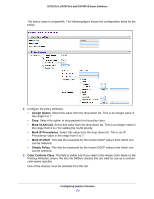
GS716Tv3, GS724Tv4, and GS748Tv5 Smart Switches IPv6 Class Configuration The IPv6 Class Configuration feature extends the existing QoS ACL and DiffServ functionality by providing support for IPv6 packet classification. An Ethernet IPv6 packet is distinguished from an IPv4 packet by its unique Ethertype value, so all IPv6 classifiers include the Ethertype field. An IPv6 access list serves the same purpose as its IPv4 counterpart. Prior to the IPv6 class feature, any DiffServ class definition was assumed to apply to an IPv4 packet. That is, any match item in a class rule was interpreted in the context of an IPv4 header. An example is a class rule that specifies an L4 Port match value. With the introduction of the IPv6 match capability, it must be specified if this class rule is for IPv4 or for IPv6 packets. To facilitate this distinction, a class configuration parameter is added to specify whether a class applies to IPv4 or IPv6 packet streams. The Destination and Source IPv6 addresses use a prefix length value instead of an individual mask to qualify it as a subnet address or a host address. The flow label is a 20-bit number that is unique to an IPv6 packet, used by end stations to signify some form of quality-of-service (QoS) handling in routers. Packets that match an IPv6 classifier are only allowed to be marked using the 802.1p (COS) field or the IP DSCP field in the Traffic Class octet. IP Precedence is not defined for IPv6: this is not an appropriate type of packet marking. IPv6 ACL/DiffServ assignment is appropriate for LAG interfaces. The procedures described by an ACL or DiffServ policy are equally applicable on a LAG interface. To create a new IPv6 class: 1. Select QoS > DiffServ > Advanced > IPv6 Class Configuration. 2. Enter a class name in the Class Name field. 3. Select the class type to associate with the policy. 4. Click the Add button. The switch supports only the Class Type value All, which means all the various match criteria defined for the class should be satisfied for a packet match. All signifies the logical AND of all the match criteria. To rename an existing class: 1. Select the check box next to the configured class. 2. In the Class Name field, specify the new name. 3. Click the Apply button. To delete a class: 1. Select the check box next to the class name. 2. Click the Delete button. The same set of fields described for IPv6 ACL classification are also supported as match criteria for DiffServ classes. Prior to the introduction of IPv6 class rule fields, any layer 3 or layer 4 item was interpreted as a field in an IPv4 packet. To properly interpret the match Configuring Quality of Service 172