Netgear GS748Tv5 Software Administration Manual - Page 211
MAC Rules, To delete a MAC ACL
 |
View all Netgear GS748Tv5 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 211 highlights
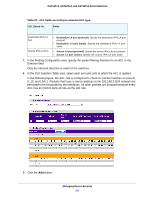
GS716Tv3, GS724Tv4, and GS748Tv5 Smart Switches To delete a MAC ACL: 1. Select the check box next to the Name field. 2. Click the Delete button. MAC Rules Use the MAC Rules screen to define rules for MAC-based ACLs. The access list definition includes rules that specify whether traffic matching the criteria is forwarded normally or discarded. A default deny all rule is the last rule of every list. Note: To create a new MAC ACL, use the MAC ACL screen. To add rules to a MAC ACL: 1. Select Security > ACL > Basic > MAC Rules. 2. From the ACL Name list, select the MAC ACL for which to create or update a rule. 3. In the Rule ID field, specify ID for the rule. 4. Configure the ACL rule criteria by selecting options or specifying values as follows: • Action. Specify what action should be taken if a packet matches the rule's criteria: - Permit. Forwards packets that meet the ACL criteria. - Deny. Drops packets that meet the ACL criteria. • Assign Queue. Specifies the hardware egress queue identifier used to handle all packets matching this ACL rule. Enter an identifying number from 0-7 in this field. • Redirect Interface. Specifies the specific egress interface where the matching traffic stream is forced, bypassing any forwarding decision normally performed by the device. • Match Every. Requires a packet to match the criteria of this ACL. Select True or False from the drop-down menu. Match Every is exclusive to the other filtering rules, so if Match Every is True, the other rules on the screen are not available. • CoS. Requires a packet's class of service (CoS) to match the CoS value listed here. Enter a CoS value between 0-7 to apply this criteria. • Destination MAC. Requires an Ethernet frame's destination port MAC address to match the address listed here. Enter a MAC address in this field. The valid format is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx. • Destination MAC Mask. If desired, enter the MAC Mask associated with the Destination MAC to match. The MAC address mask specifies which bits in the destination MAC to compare against an Ethernet frame. Use Fs and zeros in the MAC mask, which is in a wildcard format. An F means that the bit is not checked, and a zero in a bit position means that the data must equal the value given for that bit. For example, if the MAC address is aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff, and the mask is 00:00:ff:ff:ff:ff, all Managing Device Security 211