Motorola WA840GP User Guide - Page 11
Wireless Range, Technical Specifications, Type of Networks, Data Rate, Open Area, Closed Area, 5 Mbps - access point
 |
UPC - 612572118740
View all Motorola WA840GP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 11 highlights
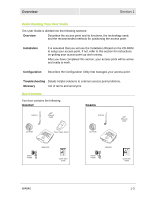
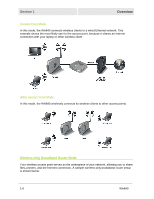
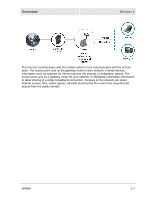
Overview Section 1 ƒ If possible, position your access point so there is a direct line of sight between the access point and your other home network devices. ƒ Avoid placing the access point next to large solid objects like computer cases, monitors, walls, fireplaces, etc. This helps the signal penetrate more cleanly. ƒ Other wireless devices like televisions, radios, microwaves and 2.4 GHz cordless telephones can interfere with the signal. Keep devices away from the access point. ƒ Mirrors, especially silver-coated, can reduce transmission performance. Wireless Range The following describes different scenarios for the expected range of the coverage area of the access point. This table is only a guide and coverage varies due to local conditions. Data Rate 54 Mbps 11 Mbps 5.5 Mbps 2 or 1 Mbps Open Area Up to 100 feet (30 m) Up to 900 feet (275 m) Up to 1300 feet (396 m) Up to 1500 feet (457 m) Closed Area Up to 60 feet (18 m) Up to 160 feet (49 m) Up to 200 feet (61 m) Up to 300 feet (91 m) Technical Specifications Your wireless access point uses a radio transmission technology defined by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) called 802.11 or Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity). This standard is subdivided into distinct categories of speed and the frequency spectrum used, designated by the lower case letter after the standard. For example, your access point supports both the 'b' and 'g' specifications. The 802.11b specification transmits data rates up to 11 Mbps while the 802.11g specification transmits data rates up to 54 Mbps. These are theoretical speeds so your performance may vary. The radio waves radiate out in a donut-shaped pattern. The waves travel through walls and floors, but transmission power and distance are affected. The theoretical distance limit is 1,000 feet (305 meters), but actual throughput and distance varies. Both standards operate in the 2.4 GHz range, meaning other electrical appliances also might interfere with the access point - televisions, radios, microwave ovens, and 2.4 GHz cordless telephones. Thus positioning your access point where it encounters the least interference gains the greatest benefit to maintaining a quality connection. Type of Networks Your access point can be used in several ways. The following examples illustrate the flexibility of your WA840. Some examples require additional hardware. WA840 1-5