Motorola WA840GP User Guide - Page 86
Arbitrary Inter-Frame Space Number AISFN, Transmit Opportunity Limit TXOP limit
 |
UPC - 612572118740
View all Motorola WA840GP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 86 highlights
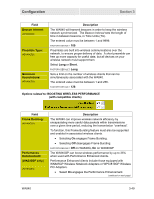
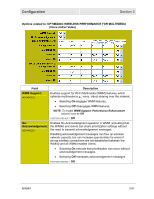
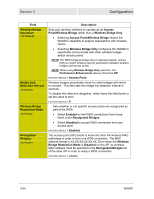
Section 3 Configuration Field EDCA AP and Client Parameters: (ADVANCED) Description WMM uses a protocol called Enhanced Distributed Channel Access (EDCA) to prioritize traffic on the wireless network. EDCA requires that wireless devices assign each intended transmission a priority, within an Access Category (AC). WMM defines 4 Access Categories: • Voice, to give voice traffic the highest priority, since it has the least tolerance for delays and/or loss of data. • Video, to give video a higher priority than other traffic, and optimize real-time video display. • Best Effort, for legacy devices, and/or any other traffic sensitive to delays (e.g., general Internet surfing). • Background, for lowest priority traffic with limited sensitivity to delays (e.g., printing). EDCA manages queues of transmissions within each of these ACs, allocating "slots" of time (or "transmit opportunities") to each, based on three prioritization settings, set per AC: • Arbitrary Inter-Frame Space Number (AISFN), a minimum number of "slots" a transmission will wait in between transmission opportunities. • Contention Window (CW), a minimum and maximum number of "slots" randomly added to the AIFSN, in order to minimize conflicts between transmissions. • Transmit Opportunity Limit (TXOP limit), the length of time allocated to a transmission one it reaches the top of a queue. For example, video is typically given larger TXOP limits because it is more data-intensive. The WA840 manages EDCA prioritization across the network. (continued on next page) 3-52 WA840