3Ware 7000-2 User Guide - Page 173
3Ware 7000-2 - Escalade RAID Controller Manual
 |
UPC - 693494700022
View all 3Ware 7000-2 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 173 highlights
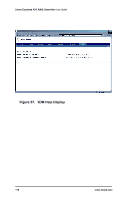
Troubleshooting Q8: Under Windows NT, disks show up at boot time but don't show up in Disk Administrator. The driver has not been installed. See "Installing the ATA RAID controller on systems that boot from a different device" on page 74. Q9: An array shows up as incomplete in the Disk Array Configuration Utility's main display similar to the following: Array Unit 1 - Incomplete 6.5 GB Port 1 - FUJITSU MPC3065AH 6.5 GB The array has some but not all of its members available. The array will be unusable. If this array is your boot device, your machine will not boot. You must either find the missing disk and replace it to complete the array, or release the member disks by deleting the incomplete array(s) listed in the display. Remember that deleting a disk array overwrites any existing data on the member drives. Q10: Under Windows NT, disks don't appear in the Windows Explorer, but appear in the 3ware BIOS scrolling messages and appear in the Disk Array Configuration Utility's main display. Log in as the administrator. Partition and format any new disk arrays or freed disks using Disk Administrator. Choose Programs from the Start menu, followed by Administrative Tools and Disk Administrator. Q11: The use of Red Hat's Disk Druid partitioning utility with Red Hat 6.2 or 7.0 is limited to 112 GB. Use fdisk if more storage capacity is required. Q12: I have created partitions over 70G but FDISK seems to think that I have a 6G partition. Windows 98 FDISK uses 16 bit integers to store the number of megabytes for each storage device. The largest capacity it can display correctly is 65,353MB. For example, 37G in hex is 08BBA and if you stripe two drives to create a 74G partition, the lower 16 bit is 1774. Hex to decimal conversion of 1774 is 6004MB (6G). www.3ware.com 173