Dell Broadcom NetXtreme Family of Adapters Broadcom NetXtreme II Network Adapt - Page 104
Checksum Offload, IEEE 802.1p QoS Tagging, Large Send Offload, TCP Offload Engine TOE
 |
View all Dell Broadcom NetXtreme Family of Adapters manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 104 highlights
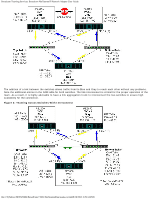
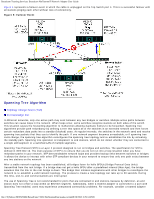
Broadcom Teaming Services: Broadcom NetXtreme II Network Adapter User Guide IEEE 802.1Q VLANs Wake On LAN Preboot Execution Environment Before creating a team, adding or removing team members, or changing advanced settings of a team member, make sure each team member has been configured similarly. Settings to check include VLANs and QoS Packet Tagging, Jumbo Frames, and the various offloads. Advanced adapter properties and teaming support are listed in Table 7. Table 7: Advanced Adapter Properties and Teaming Support Adapter Properties Supported by Teaming Virtual Adapter Checksum Offload Yes IEEE 802.1p QoS Tagging No Large Send Offload Yesa TCP Offload Engine (TOE) Yesb, c Jumbo Frames Yesb IEEE 802.1Q VLANs Yesc Wake on LAN Nod Preboot Execution environment (PXE) Yese a All adapters on the team must support this feature. Some adapters may not support this feature if ASF/IPMI is also enabled. b Must be supported by all adapters in the team. c Only for Broadcom adapters. d See Wake On LAN. e As a PXE sever only, not as a client. A team does not necessarily inherit adapter properties; rather various properties depend on the specific capability. For instance, an example would be flow control, which is a physical adapter property and has nothing to do with BASP, and will be enabled on a particular adapter if the miniport driver for that adapter has flow control enabled. NOTE: All adapters on the team must support the property listed in Table 7 in order for the team to support the property. Checksum Offload Checksum Offload is a property of the Broadcom network adapters that allows the TCP/IP/UDP checksums for send and receive traffic to be calculated by the adapter hardware rather than by the host CPU. In high-traffic situations, this can allow a system to handle more connections more efficiently than if the host CPU were forced to calculate the checksums. This property is inherently a hardware property and would not benefit from a software-only implementation. An adapter that supports Checksum Offload advertises this capability to the operating system so that the checksum does not need to be calculated in the protocol stack. Checksum Offload is only supported for IPv4 at this time. IEEE 802.1p QoS Tagging The IEEE 802.1p standard includes a 3-bit field (supporting a maximum of 8 priority levels), which allows for traffic prioritization. The BASP intermediate driver does not support IEEE 802.1p QoS tagging. Large Send Offload Large Send Offload (LSO) is a feature provided by Broadcom network adapters that prevents an upper level protocol such as TCP from breaking a large data packet into a series of smaller packets with headers appended to them. The protocol stack need only generate a single header for a data packet as large as 64 KB, and the adapter hardware breaks the data buffer into appropriately-sized Ethernet frames with the correctly sequenced header (based on the single header originally provided). TCP Offload Engine (TOE) The TCP/IP protocol suite is used to provide transport services for a wide range of applications for the Internet, LAN, and for file:///T|/htdocs/NETWORK/BroadCom/71921/NetXtremeII/en/teamsvcs.htm[9/26/2012 3:29:14 PM]