Dell Broadcom NetXtreme Family of Adapters Broadcom NetXtreme II Network Adapt - Page 95
Teaming Support by Processor, Configuring Teaming, Supported Features by Team Type, Repeater Hub
 |
View all Dell Broadcom NetXtreme Family of Adapters manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 95 highlights
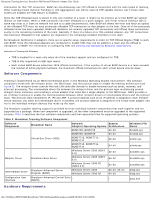
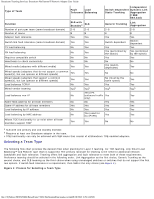
Broadcom Teaming Services: Broadcom NetXtreme II Network Adapter User Guide Repeater Hub Switching Hub Router The various teaming modes described in this document place certain restrictions on the networking equipment used to connect clients to teamed systems. Each type of network interconnect technology has an effect on teaming as described in the following sections. Repeater Hub A Repeater Hub allows a network administrator to extend an Ethernet network beyond the limits of an individual segment. The repeater regenerates the input signal received on one port onto all other connected ports, forming a single collision domain. This means that when a station attached to a repeater sends an Ethernet frame to another station, every station within the same collision domain will also receive that message. If two stations begin transmitting at the same time, a collision occurs, and each transmitting station must retransmit its data after waiting a random amount of time. The use of a repeater requires that each station participating within the collision domain operate in half-duplex mode. Although half-duplex mode is supported for Gigabit Ethernet adapters in the IEEE 802.3 specification, half-duplex mode is not supported by the majority of Gigabit Ethernet adapter manufacturers. Therefore, half-duplex mode is not considered here. Teaming across hubs is supported for troubleshooting purposes (such as connecting a network analyzer) for SLB teams only. Switching Hub Unlike a repeater hub, a switching hub (or more simply a switch) allows an Ethernet network to be broken into multiple collision domains. The switch is responsible for forwarding Ethernet packets between hosts based solely on Ethernet MAC addresses. A physical network adapter that is attached to a switch may operate in half-duplex or full-duplex mode. To support Generic Trunking and 802.3ad Link Aggregation, a switch must specifically support such functionality. If the switch does not support these protocols, it may still be used for Smart Load Balancing. NOTE: All modes of network teaming are supported across switches when operating as a stackable switch. Router A router is designed to route network traffic based on Layer 3 or higher protocols, although it often also works as a Layer 2 device with switching capabilities. The teaming of ports connected directly to a router is not supported. Teaming Support by Processor All team types are supported by the IA-32 and EM64T processors. Configuring Teaming The Broadcom Advanced Control Suite utility is used to configure teaming in the supported operating system environments. The Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BACS) utility is designed to run on 32-bit and 64-bit Windows family of operating systems. BACS is used to configure load balancing and fault tolerance teaming, and VLANs. In addition, it displays the MAC address, driver version, and status information about each network adapter. BACS also includes a number of diagnostics tools such as hardware diagnostics, cable testing, and a network topology test. Supported Features by Team Type Table 4 provides a feature comparison across the team types supported by Dell. Use this table to determine the best type of team for your application. The teaming software supports up to eight ports in a single team and up to four teams in a single system. The four teams can be any combination of the supported teaming types, but each team must be on a separate network or subnet. Table 4: Comparison of Team Types Switch- file:///T|/htdocs/NETWORK/BroadCom/71921/NetXtremeII/en/teamsvcs.htm[9/26/2012 3:29:14 PM]