Dell Broadcom NetXtreme Family of Adapters Broadcom NetXtreme II Network Adapt - Page 154
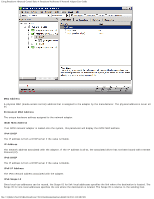
Diagnostic Tests, Diagnostics, Result, Select a test to run, Select All, Clear All, Number of loops
 |
View all Dell Broadcom NetXtreme Family of Adapters manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 154 highlights
Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4: Broadcom NetXtreme II Network Adapter User Guide The Diagnostic Tests option on the Diagnostics tab lets you check the state of the physical components on a Broadcom network adapter. You can trigger the tests manually, or choose to have BACS continuously perform them. If the test are performed continuously, then the number of passes and fails in the Result field for each test increments every time the tests are performed. For example, if a test is performed four times and there are no fails, the value in the Result field for that test is 4/0. However, if there were 3 passes and 1 fail, the value in the Result field is 3/1. NOTES: You must have administrator privileges to run diagnostic tests. The network connection is temporarily lost while these tests are running. Some tests are not supported on all Broadcom adapters. To run the diagnostic tests once 1. Click the name of the adapter to test in the Explorer View pane and select the Diagnostics tab. 2. From the Select a test to run list, select Diagnostic Tests. 3. Select the diagnostic tests you want to run. Click Select All to select all tests or Clear All to clear all test selections. 4. Select the number of times to run the tests from Number of loops. 5. Click Run test(s). 6. In the error message window that warns of the network connection being temporarily interrupted, click Yes. The results are displayed in the Result field for each test. Control Registers This test verifies the read and write capabilities of the network adapter registers by writing various values to the registers and verifying the results. The adapter driver uses these registers to perform network functions such as sending and receiving information. A test failure indicates that the adapter may not be working properly. MII Registers This test verifies the read and write capabilities of the registers of the physical layer (PHY). The physical layer is used to control the electrical signals on the wire and to configure network speeds such as 1000 Mbit/s. file:///T|/htdocs/NETWORK/BroadCom/71921/NetXtremeII/en/bacs.htm[9/26/2012 3:29:48 PM]