McAfee MTP08EMB3RUA Product Guide - Page 93
Use learn mode to discover Internet applications, The role of IP addresses
 |
UPC - 731944568133
View all McAfee MTP08EMB3RUA manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
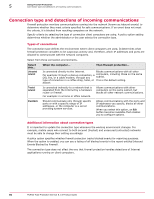
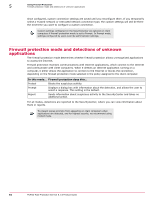
Using Firewall Protection The role of IP addresses 5 How policy options are implemented in the three protection modes Use the following table to determine how policy options are implemented in the different protection modes. Mode Behavior of firewall protection Report • Users are not prompted about detections. • Detections are reported to the SecurityCenter. • Administrator can select allowed applications, which are not reported as detections. • Can be used as a "learn" mode to discover which applications to allow and block. Prompt • Users are prompted about detections. • Detections are reported to the SecurityCenter. • Administrator can select allowed applications. These applications are not reported as detections, and users are not prompted for a response to them. • Users can approve additional applications in response to prompts. These are reported to the SecurityCenter. Protect • Users are not prompted about detections. • Users are notified about blocked applications. • Detections are reported to the SecurityCenter. • Administrator can select allowed applications, which are not reported as detections. If the policy is changed from Prompt mode to Protect mode or Report mode, firewall protection saves user settings for allowed applications. If the policy is then changed back to Prompt mode, these settings are reinstated. Use learn mode to discover Internet applications Report mode can be used as a "learn mode" to help you determine which applications to allow. In Report mode, firewall protection tracks but does not block unrecognized Internet applications. You can review detected applications in the Unrecognized Programs report and approve those that are appropriate for your policy. When you no longer see applications you want to allow in the report, change the policy setting to Prompt or Protect mode. The role of IP addresses An IP address is used to identify any device that originates or receives a request or a message over networks and the Internet (which comprises a very large group of networks). Each IP address uses a unique set of hexadecimal characters to identify a network, a subnetwork (if applicable), and a device within the network. An IP address enables: • The request or message to be delivered to the correct destination. • The receiving device to know where the request or message originated and where to send a response if one is required. McAfee Total Protection Service 5.1.5 Product Guide 93