ZyXEL NWA-3163 User Guide - Page 145
How STP Works, 3.1.4, STP Port States
 |
View all ZyXEL NWA-3163 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 145 highlights
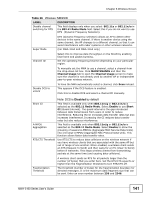
Chapter 8 Wireless Screen 8.3.1.3 How STP Works After a bridge determines the lowest cost-spanning tree with STP, it enables the root port and the ports that are the designated ports for connected LANs, and disables all other ports that participate in STP. Network packets are therefore only forwarded between enabled ports, eliminating any possible network loops. STP-aware bridges exchange Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) periodically. When the bridged LAN topology changes, a new spanning tree is constructed. Once a stable network topology has been established, all bridges listen for Hello BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units) transmitted from the root bridge. If a bridge does not get a Hello BPDU after a predefined interval (Max Age), the bridge assumes that the link to the root bridge is down. This bridge then initiates negotiations with other bridges to reconfigure the network to re-establish a valid network topology. 8.3.1.4 STP Port States STP assigns five port states (see next table) to eliminate packet looping. A bridge port is not allowed to go directly from blocking state to forwarding state so as to eliminate transient loops. Table 28 STP Port States PORT STATES DESCRIPTIONS Disabled STP is disabled (default). Blocking Only configuration and management BPDUs are received and processed. Listening All BPDUs are received and processed. Learning All BPDUs are received and processed. Information frames are submitted to the learning process but not forwarded. Forwarding All BPDUs are received and processed. All information frames are received and forwarded. 8.3.2 DFS When you choose 802.11a or 802.11n/a in Access Point mode, the NWA uses DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) to give you a wider choice of wireless channels. DFS allows you to use channels in the frequency range normally reserved for radar systems. Radar uses radio signals to detect the location of objects for military, meteorological or air traffic control purposes. As long as your NWA detects no radar activity on the channel you select, you can use the channel to communicate. However, a wireless LAN operating on the same frequency as an active radar system could disrupt the radar system. Therefore, if the NWA detects radar NWA-3160 Series User's Guide 145