ZyXEL NWA-3163 User Guide - Page 154
WMM QoS Priorities
 |
View all ZyXEL NWA-3163 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 154 highlights
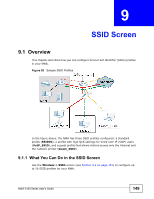
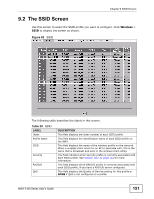
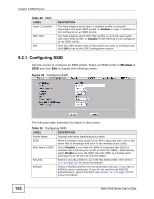
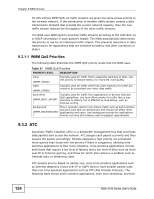
Chapter 9 SSID Screen On APs without WMM QoS, all traffic streams are given the same access priority to the wireless network. If the introduction of another traffic stream creates a data transmission demand that exceeds the current network capacity, then the new traffic stream reduces the throughput of the other traffic streams. The NWA uses WMM QoS to prioritize traffic streams according to the IEEE 802.1q or DSCP information in each packet's header. The NWA automatically determines the priority to use for an individual traffic stream. This prevents reductions in data transmission for applications that are sensitive to latency and jitter (variations in delay). 9.3.1.1 WMM QoS Priorities The following table describes the WMM QoS priority levels that the NWA uses. Table 31 WMM QoS Priorities PRIORITY LEVEL DESCRIPTION voice (WMM_VOICE) Typically used for traffic that is especially sensitive to jitter. Use this priority to reduce latency for improved voice quality. video (WMM_VIDEO) Typically used for traffic which has some tolerance for jitter but needs to be prioritized over other data traffic. best effort (WMM_BEST_EFFORT ) Typically used for traffic from applications or devices that lack QoS capabilities. Use best effort priority for traffic that is less sensitive to latency, but is affected by long delays, such as Internet surfing. background (WMM_BACKGROUND ) This is typically used for non-critical traffic such as bulk transfers and print jobs that are allowed but that should not affect other applications and users. Use background priority for applications that do not have strict latency and throughput requirements. 9.3.2 ATC Automatic Traffic Classifier (ATC) is a bandwidth management tool that prioritizes data packets sent across the network. ATC assigns each packet a priority and then queues the packet accordingly. Packets assigned a high priority are processed more quickly than those with low priority if there is congestion, allowing timesensitive applications to flow more smoothly. Time-sensitive applications include both those that require a low level of latency and a low level of jitter such as Voice over IP or Internet gaming, and those for which jitter alone is a problem such as Internet radio or streaming video. ATC assigns priority based on packet size, since time-sensitive applications such as Internet telephony (Voice over IP or VoIP) tend to have smaller packet sizes than non-time sensitive applications such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol). The following table shows some common applications, their time sensitivity, and their 154 NWA-3160 Series User's Guide