Epson LQ 1050 User Manual - Page 98
Defining Your Own Characters, Data numbers, of eight bits. Hence, one bit represents each dot.
 |
View all Epson LQ 1050 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
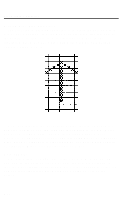
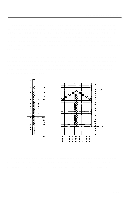
User-Defined Characters Defining Your Own Characters The first step in defining characters is to place the dots on a grid just as you want them to print. The examples here, like the ones in the graphics section, use an x to represent each dot. In the illustration below you see a draft grid with a simple user-defined character planned on it. Now you translate the dot pattern you've created on paper to a numeric format so you can send the information to the LQ. Every dot has an assigned value. Each vertical column (which has a maximum of 24 dots) is first divided into three groups of eight dots. Each group of eight dots is represented by one byte, which consists of eight bits. Hence, one bit represents each dot. Data numbers The bits within each byte have values of 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128. In the vertical column of dots, the bits are arranged so that the most significant bit (which has a value of 128) is at the top and the least significant bit (which has a value of 1) is at the bottom. 4-22