HP StorageWorks MSA 2/8 HP StorageWorks Fabric Watch V3.1.x/4.1.x User Guide ( - Page 40
Monitoring Tools, Counters, Thresholds, Naming Conventions
 |
View all HP StorageWorks MSA 2/8 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 40 highlights
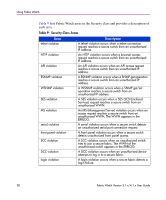
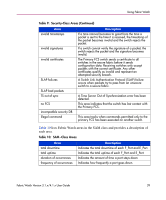
Using Fabric Watch Monitoring Tools Fabric Watch uses a number of tools to: ■ Monitor switch performance. ■ Monitor fabric performance. ■ Alert SAN managers to potential problems. Counters Counters represent the value of a behavior variable. Counters can be cumulative or current. A counter may represent the total number of times that a given error occurred since Fabric Watch began logging occurrences of that error, or it may represent the current value of a particular behavior (such as fan speed or chassis temperature). Fabric Watch compares counter values to threshold values to determine when events occur. Thresholds Thresholds consist of traits, behaviors, and alarms, some optional, some required. Fabric Watch uses these components to determine how and when to check the status of a variable. Fabric Watch groups these components and identifies them as a threshold to efficiently report errors to SAN administrators. Thresholds identify values or ranges of values to which Fabric Watch compares counters to determine if a given element warrants an alarm. You can configure different boundaries to establish different types of thresholds. Naming Conventions You can identify a Fabric Watch threshold by its unique name. Threshold names consist of the following three parts, with no separators: ■ class name abbreviation ■ area name abbreviation ■ element index number You can reference this standard naming format to identify elements in error messages. Each error message references the relevant element by class, area, and number. 40 Fabric Watch Version 3.1.x/4.1.x User Guide