HP StorageWorks MSA 2/8 HP StorageWorks Fabric Watch V3.1.x/4.1.x User Guide ( - Page 44
Traits, Table 13: Threshold Traits, Behaviors, Table 13
 |
View all HP StorageWorks MSA 2/8 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 44 highlights
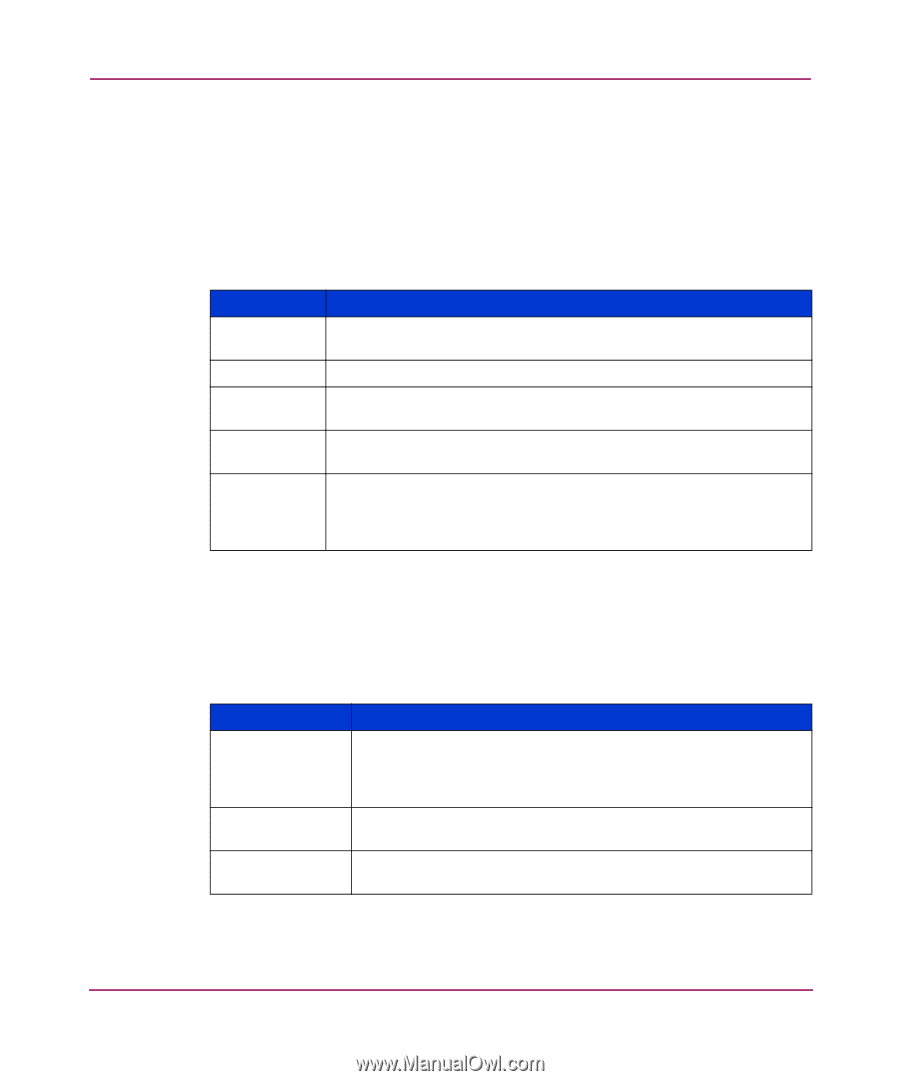
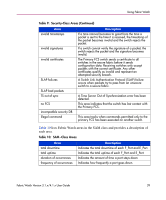
Using Fabric Watch Traits Behaviors Traits are the characteristics that define a threshold. Traits are area-based. When you configure a boundary, that boundary applies to every element in an area. Traits are non-volatile. You do not need to reconfigure traits when you restart a switch. Table 13 lists the traits that can define a threshold and what each trait identifies. Table 13: Threshold Traits Trait unit string time base low boundary high boundary buffer size Definition Unit of measurement that Fabric Watch alarms use to display the value of a particular counter. Basic unit of time in which Fabric Watch records events. Lowest limit at which the value of a counter does not register an event. Highest limit at which the value of a counter does not register an event. Size of a threshold buffer. The buffer size determines the distance between the upper buffer and the upper boundary, and the distance between the lower buffer and the lower boundary. The buffer size establishes the buffer zones (see Figure 1 on page 48). Threshold behavior defines if and when an event registers against a given threshold. These behaviors are element-based, so you must configure traits for each individual element. Table 14 lists and explains threshold behaviors. Table 14: Threshold Behavior Behavior status behavior type behavior interval Description Configures a threshold as enabled (active) or disabled (inactive). Fabric Watch enables thresholds by default. Status is non-volatile. You can disable thresholds permanently because the setting persists after the switch reboots. Configures a threshold as continuous or triggered. By default, Fabric Watch only monitors triggered events. Configures the minimum time interval (in seconds) between two instances of the same type of alarm. 44 Fabric Watch Version 3.1.x/4.1.x User Guide