D-Link DGS-3426 User Manual - Page 47
IPv6, Overview
 |
View all D-Link DGS-3426 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 47 highlights
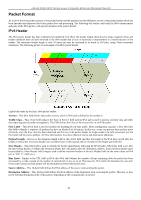
xStack DGS-3400 Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch IPv6 The xStack DGS-3400 has the capability to support the following: • IPv6 unicast, multicast and anycast addresses • Allow for IPv6 packet forwarding • IPv6 fragmentation and re-assembly • Processing of IPv6 packet and extension headers • Static IPv6 route configuration • IPv6 Neighbor Discovery • Link-Layer Address resolution, Neighbor Unreachability Detection and Duplicate Address Detection over broadcast mediums (ex: Ethernet) • Send Router Advertisement • ICMPv6 functionality The following sections will briefly explain IPv6, its functionality and how IPv6 is implemented on this Switch. Overview IP version 6 is the logical successor to IP version 4. It was known that IPv4 could not support the amount of addresses that would eventually be needed for not only each person, but each device that would require an IP address, and therefore a system with a larger pool of IP addresses was required. IPv6 has addressed that issue, along with other issues that enhance routing over the network, provide better security and improve Quality of Service for Internet users. Some of the improvements made were: Expanding the Capabilites for IP Addressing - IPv6 has increased the size of the IP address from 32 bits to 128 bits. As a result, the addressing hierarchy has been greatly expanded, more nodes now have the capability of having a unique IP address and the method of assigning an IP address to an interface has become cleaner and quicker. Unicast and multicast addresses still exist but in a purer form and multicast addresses now have a scope field which increases the scalability of multicast routing. Also, an anycast address has been added, which will send packets to the closest node which is a part of a group of nodes, thereby eliminating a specified device for a particular group. Simplifying the Packet Header - The IPv6 packet header has been simplified from IPv4 as some headers have been modified or dropped altogether, which improves processing speed and cost. The IPv6 header now has a fixed length of 40 bytes consisting of an 8-byte header and two 16-byte IP addresses (source and destination). Extensions and Options Enhancement - Packet header option fields encoding has been enhanced to allow for proficient forwarding of packets due to lesser restrictions on packet option length and encoding method. This enhancement will also allow new option fields to be integrated into the IPv6 system without hassles and limitations. These optional headers are placed between the header and the payload of a packet, if they are necessary at all. Authentication and Privacy Extension Support - New authentication capabilities use extensions for data integrity and data confidentiality for IPv6. Flow Labeling - This new capability allows packets to be streamlined into certain traffic "flows" if labeled by the sender. In this way, services such as "real time services or non-default quality of service can receive special attention for improved flow quality. 33