Dell PowerEdge M520 Dell PowerConnect M6220/M6348/M8024 Switches Configuration - Page 101
Guest VLAN, CLI Examples, Tunnel-Type=VLAN 13
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge M520 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 101 highlights
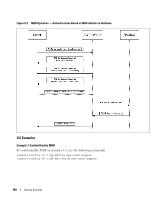
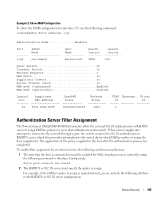
Much of the configuration to assign hosts to a particular VLAN takes place on the RADIUS server or 802.1X authenticator. If you use an external RADIUS server to manage VLANs, you configure the server to use Tunnel attributes in Access-Accept messages in order to inform the switch about the selected VLAN. These attributes are defined in RFC 2868, and their use for dynamic VLAN is specified in RFC 3580. The VLAN attributes defined in RFC3580 are as follows: • Tunnel-Type=VLAN (13) • Tunnel-Medium-Type=802 • Tunnel-Private-Group-ID=VLANID VLANID is 12-bits and has a value between 1 and 4093. Guest VLAN The Guest VLAN feature allows a switch to provide a distinguished service to unauthenticated users. This feature provides a mechanism to allow visitors and contractors to have network access to reach external network with no ability to browse information on the internal LAN. In port-based 802.1X mode, when a client that does not support 802.1X is connected to an unauthorized port that is 802.1X-enabled, the client does not respond to the 802.1X requests from the switch. Therefore, the port remains in the unauthorized state, and the client is not granted access to the network. If a guest VLAN is configured for that port, then the port is placed in the configured guest VLAN and the port is moved to the authorized state, allowing access to the client. However, if the port is in MAC-based 802.1X authentication mode, it will not move to the authorized state. MAC-based mode makes it possible for both authenticated and guest clients to use the same port at the same time. Client devices that are 802.1X-supplicant-enabled authenticate with the switch when they are plugged into the 802.1X-enabled switch port. The switch verifies the credentials of the client by communicating with an authentication server. If the credentials are verified, the authentication server informs the switch to 'unblock' the switch port and allows the client unrestricted access to the network; i.e., the client is a member of an internal VLAN. Beginning with software release 2.1, Guest VLAN Supplicant mode is configured on a per-port basis. If a client does not attempt authentication on a port and the port is configured for Guest VLAN, the client is assigned to the guest VLAN configured on that port. The port is assigned a Guest VLAN ID and is moved to the authorized status. Disabling the supplicant mode does not clear the ports that are already authorized and assigned Guest VLAN IDs. CLI Examples The following examples show how to configure the switch to accept RADIUS-assigned VLANs and Guest VLANs. The examples assume that the RADIUS server and VLAN information has already been configured on the switch. For information about how to configure VLANs, see "Virtual LANs" on page 25. Device Security 101