Dell PowerEdge M520 Dell PowerConnect M6220/M6348/M8024 Switches Configuration - Page 87
Using the Web Interface to Con RIP, Route Preferences
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge M520 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 87 highlights
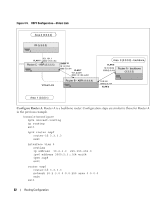
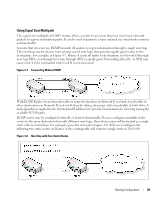
Using the Web Interface to Configure RIP Use the following screens to perform the same configuration using the Graphical User Interface: • Routing > IP > Configuration> To enable routing for the switch. • Routing > IP > Interface Configuration > To configure the VLAN routing interfaces. • Routing > RIP > Configuration. To enable RIP for the switch. • Routing > RIP > Interface Configuration. To enable RIP for the VLAN routing interfaces and specify the RIP versions. Route Preferences You can use route preference assignment to control how the router chooses which routes to use when alternatives exist. This section describes three uses of route preference assignment: • "Assigning Administrative Preferences to Routing Protocols" on page 87 • "Using Equal Cost Multipath" on page 89 Assigning Administrative Preferences to Routing Protocols The router may learn routes from various sources: static configuration, local route discovery, RIP, and OSPF. Most routing protocols use a route metric to determine the shortest path known to the protocol; however, these metrics are independent of one another and not easily comparable. Therefore, when the router learns a route to a particular destination from two different sources, the metrics do not provide a means of choosing the best route for your network. The PowerConnect M6220/M6348/M8024 switches enable you to identify the preferred route type by assigning an administrative preference value to each type. The values are arbitrary (1 to 255); however, a route type that has a lower value is preferred over higher-value types. Local routes are assigned an administrative preference value of 0 and are always preferred over other route types to local hosts. Static routes have a default value of 1; however, this value and all other default preference values are user-configurable. A protocol can be assigned a preference value of 255 to prevent the router from forwarding packets using that protocol. For routed management traffic: 1 Router entries are checked for applicable destinations. 2 The globally assigned default-gateway is consulted. Router entries take precedence over an assigned default-gateway. Routing Configuration 87