HP BladeSystem bc2800 Administrator's Guide HP Session Allocation Manager (HP - Page 18
Setting up a User with Static (Dedicated) Resources, Connect, Available, In Use - blade specifications
 |
View all HP BladeSystem bc2800 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 18 highlights
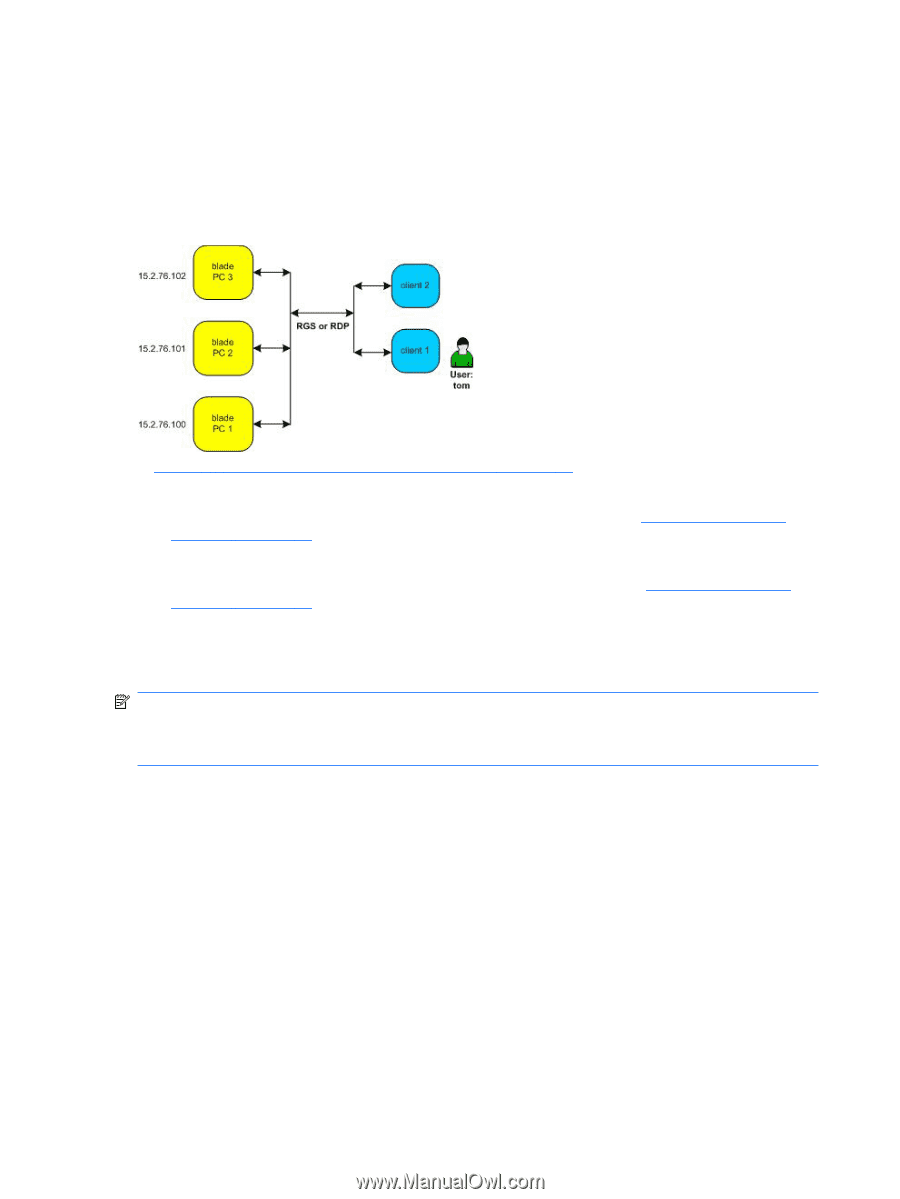
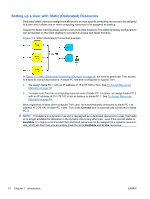
Setting up a User with Static (Dedicated) Resources Dedicated (static) resource assignment allows one or more specific computing resources to be assigned to a user and it allows one or more computing resources to be assigned as backup. Support for Static roaming allows users to work from other locations. The differing display configurations can be stacked on the client desktop to provide full access with fewer monitors. Figure 1-3 Static (Dedicated) Connection Example In Figure 1-3 Static (Dedicated) Connection Example on page 10, we need to grant user Tom access to a specific computing resource. A blade PC has been configured to support Tom. 1. We assign blade PC 1 with an IP address of 15.2.76.100 to Tom. See To Assign Resources Manually on page 58. 2. To make sure Tom has a computing resource even if blade PC 1 is down, we assign blade PC 3 with an IP address of 15.2.76.102 to act as backup to blade PC 1. See To Assign Resources Manually on page 58. Now, regardless of what client computer Tom uses, he is automatically connected to blade PC 1 at address 15.2.76.100. If blade PC 1 fails, Tom clicks Connect and is automatically connected to blade PC 3. NOTE: If a blade is in a dynamic role and is reassigned as a dedicated resource to a user, that blade is no longer available for allocation in the dynamic role to any other user, even if the current status is Available. It is highly recommended that dedicated resources not be assigned to a dynamic resource role, which will then help you accurately track the list of Available and In Use resources. 10 Chapter 1 Introduction ENWW