Creative 70EM896106000 Owners Manual - Page 68
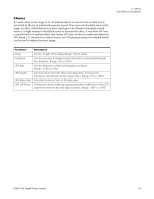
Compressor, Basic Controls, Threshold, Ratio, Attack, Release, Post Gain
 |
UPC - 054651126893
View all Creative 70EM896106000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 68 highlights
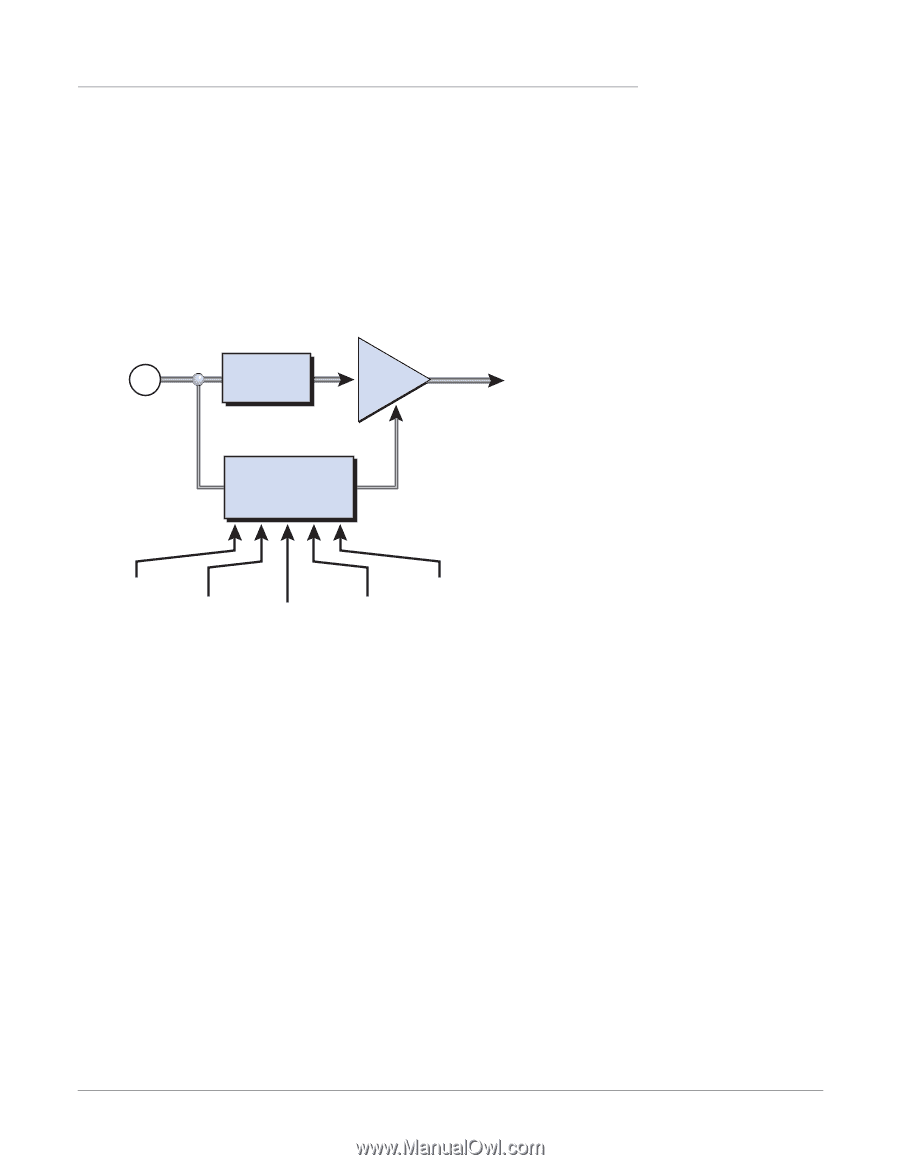
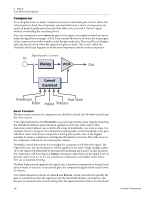
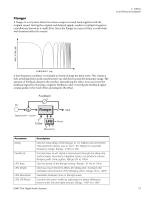
5 - Effects Core Effects Descriptions Compressor In its simplest form, an audio compressor is just an automatic gain control. When the volume gets too loud, the compressor automatically turns it down. Compressors are useful in musical applications because they allow you to record a "hotter" signal without overloading the recording device. Since the compressor turns down the gain of the signal, you might wonder how can it make the signal level stronger. A Post Gain control allows you to boost the output gain of the compressor in order to make up for the gain reduction. The overall level is higher and only turned down when the signal level gets too loud. This level is called the Threshold, which just happens to be the most important control on the compressor. Signal path = Stereo In Delay VCA Out Level Control Threshold Post Gain Ratio Attack Release Basic Controls The three main controls of a compressor are the Ratio control, the Threshold control and the Gain control. If the signal falls below the Threshold, no processing will take place. Signals exceeding the Threshold will have gain reduction applied as set by the ratio control. This important control allows you to dial in the range of amplitudes you want to tame. For example, if you're trying to trim off just the loudest peaks, set the threshold so the gain reduction meter only shows compression during these peaks. One of the biggest mistakes in using a compressor is having the threshold set too low. This adds noise as the compressor will always be reducing the volume. The Ratio control determines how strongly the compressor will affect the signal. The higher the ratio, the more reduction will be applied. If the ratio is high enough, (above 10:1) the signal will effectively be prevented from getting any louder. In this situation, the compressor will be acting as a Limiter, placing an upper limit on the signal level. In general, ratios from 2:1 to 6:1 are considered compression and higher ratios above 10:1 are considered limiting. The Post Gain control amplifies the signal after it has been compressed to bring it back up in volume. If you don't increase the gain, the compressed signal will be much lower in volume. Two other important controls are Attack and Release. Attack controls how quickly the gain is turned down after the signal exceeds the threshold. Release controls how fast the gain is returned to its normal setting after the signal has fallen below the threshold 68 Creative Professional