Creative 70EM896106000 Owners Manual - Page 79
Stereo Reverb
 |
UPC - 054651126893
View all Creative 70EM896106000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 79 highlights
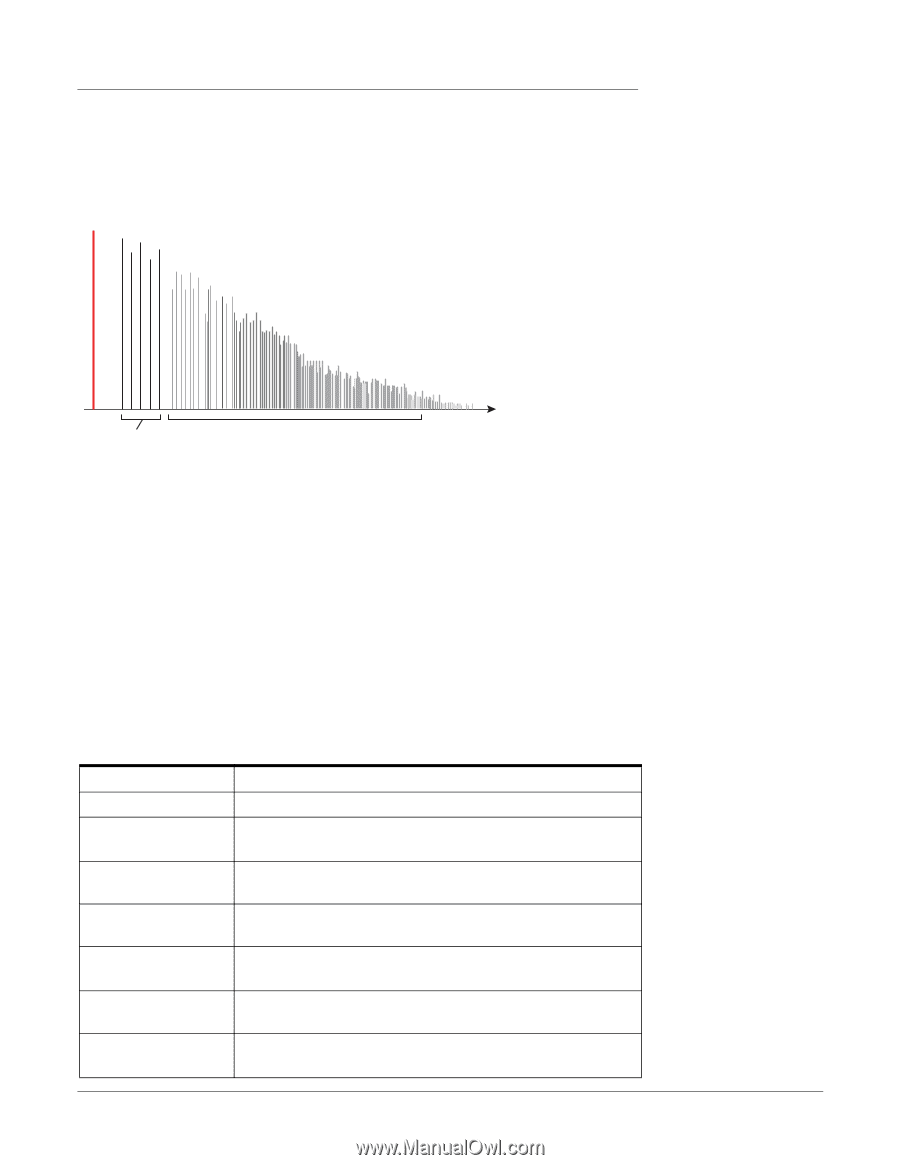
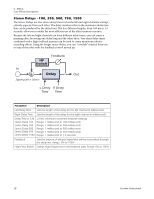
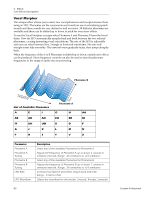
Stereo Reverb Reverberation is a simulation of a natural space such as a room or hall. The stereo reverb algorithm is designed to simulate various halls, rooms and reverberation plates. Decay time defines the time it takes for the reflected sound from the room to decay or die away. The diagram below shows a generalized reverberation envelope. 5 - Effects Core Effects Descriptions Early Reflections Late Reverb Time After a short pre-delay period, the echoes from the closest walls or ceiling are heard. These first echoes, or early reflections, vary greatly depending on the type of room. Some time after the early reflection cluster ends (late reverb delay), the late reverberation (a dense cloud of complex wall reflections) begins and decays according to the time set by the Decay Time parameter. Diffusion is the amount of scattering and density of the late reverberation cloud. Rooms with many complex surfaces have more diffusion than bare rooms. High frequency energy tends to fade away first as a sound is dissipated in a room. The High Frequency Damping parameter adjusts the time it takes for the high frequency energy to die away and thus changes the characteristics of the room. Rooms with smooth, hard surfaces are more reflective and have less high frequency damping. Rooms filled with sound absorbing materials, such as curtains or people, have more high frequency damping. The Low Frequency Damping parameter adjusts the time it takes for the low frequencies to die away. This control adjusts the "boominess" of the room. Parameter Decay Time Early Reflections Level Early/Late Reverb Bal Late Reverb Delay Diffusion High Freq. Damping Low Freq. Damping Description Sets the length of the Late Reverb. Range 1.5 to 30 seconds Sets the volume of the initial wall reflections. Range: 0% to 100% Adjusts the balance between early refections and late reverb. Range: 0% to 100% Sets the time between early reflections and the onset of the late reverb cloud. Range: 1ms to 350ms Sets the amount of scattering of the late reverb cloud. Range: 0% to 100% Sets the rate at which high frequencies die away. Range: -10.0 to +3.0 damping factor Sets the rate at which low frequencies die away. Range: -10.0 to +3.0 damping factor E-MU PCIe Digital Audio Systems 79