Creative 70EM896106000 Owners Manual - Page 75
Mono Delays - 100
 |
UPC - 054651126893
View all Creative 70EM896106000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 75 highlights
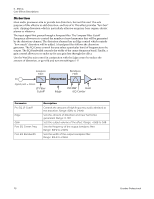
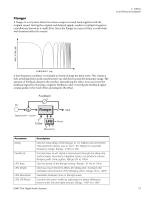
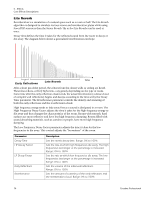
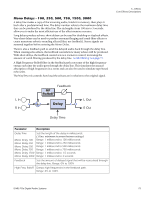
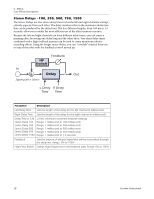
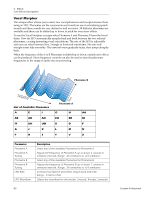
Mono Delays - 100, 250, 500, 750, 1500, 3000 A delay line makes a copy of the incoming audio, holds it in memory, then plays it back after a predetermined time. The delay number refers to the maximum delay time that can be produced by the delay line. The six lengths, from 100 ms to 3 seconds, allow you to make the most efficient use of the effect memory resource. Long delays produce echoes, short delays can be used for doubling or slapback effects. Very short delays can be used to produce resonant flanging and comb filter effects or create monotone robotic-sounding effects (Hint: use feedback). Stereo signals are summed together before entering the Mono Delay. There is also a feedback path to send the delayed audio back through the delay line. When creating echo effects, the feedback controls how many echoes will be produced. With short delays, the feedback control acts as a resonance control, increasing the amount of comb filtering produced by the delay line. Comb filtering: See page 71. A High Frequency Rolloff filter in the feedback path cuts some of the high frequency energy each time the audio goes through the delay line. This simulates the natural absorption of high frequencies in a room and can also be used to simulate tape-based echo units. The Wet/Dry mix controls how loud the echoes are in relation to the original signal. 5 - Effects Core Effects Descriptions Feedback HF Rolloff L In L Out Delay R In R Out Delay Time Parameter Description Delay Time Sets the length of the delay in milliseconds. (.01ms. minimum increment between settings) Mono Delay 100 Range: 1 millisecond to 100 milliseconds Mono Delay 250 Range: 1 millisecond to 250 milliseconds Mono Delay 500 Range: 1 millisecond to 500 milliseconds Mono Delay 750 Range: 1 millisecond to 750 milliseconds Mono Delay 1500 Range: 1 millisecond to 1.5 seconds Mono Delay 3000 Range: 1 millisecond to 3 seconds Feedback Sets the amount of delayed signal that will be recirculated through the delay line. Range: 0% to 100% High Freq. Rolloff Damps high frequencies in the feedback path. Range: 0% to 100% E-MU PCIe Digital Audio Systems 75