HP 12C#ABA hp 12c_solutions handbook_English_E.pdf - Page 164
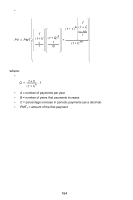
Queuing and Waiting Theory, Graduated Payment Mortgage, Average number of customers in queue.
 |
UPC - 492410746430
View all HP 12C#ABA manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 164 highlights
Queuing and Waiting Theory • n = number of servers. • λ = arrival rate of customers (Poisson input). • µ = service rate for each server (exponential service). • ρ = Intensity factor n for valid results). • P0 = Probability that all servers are idle. • Pb = Probability that all servers are busy. • Lq = Average number of customers in queue. • L = Average number of customers in the system (waiting and being served). • Tq = Average waiting time in queue. • T = Average total time through the sytem. • P(t) = Probability of waiting longer than time t. • P0 = -1 n-1 ∑k = 0 -ρk---!k- + n---------- n! 1 - n-ρ- • Pb = ------ρ---n---P-----0-----n!1 - n-ρ- • • Lq = -n-ρ---P-----b-ρ-- L = Lq + ρ T = L / λ Tq = L--λ--q- • P(t) = Pbe-(nµ - λ)t Graduated Payment Mortgage 163