HP Color LaserJet Enterprise CP4020 HP Designjet 4020 and 4520 Printer Series - Page 87
Application settings, Open Adobe InDesign and select
 |
View all HP Color LaserJet Enterprise CP4020 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 87 highlights
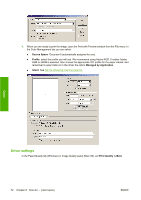
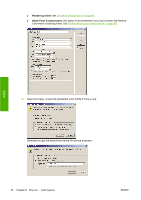
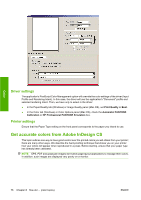
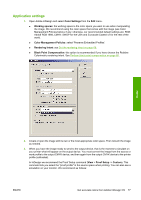
Application settings 1. Open Adobe InDesign and select Color Settings from the Edit menu. ● Working spaces: the working space is the color space you want to use when manipulating the image. We recommend using the color space that comes with the image (see Color Management Policies below), if any; otherwise, our recommended default settings are: RGB: Adobe RGB 1998, CMYK: SWOP for the USA and Euroscale Coated v2 for the rest of the world. ● Color Management Policies: select 'Preserve Embedded Profiles'. ● Rendering Intent: see Set the rendering intent on page 69. ● Black Point Compensation: this option is recommended if you have chosen the Relative Colorimetric rendering intent. See Perform black point compensation on page 68. Color 2. Create or open the image with its own or the most appropriate color space. Then retouch the image as needed. 3. When you have the image ready to send to the output device, that is the moment to simulate on your printer what will appear on the output device. You must convert the image from the source or work profile to the output CMYK device, and then again from the output CMYK device to the printer profile (calibrated). In InDesign we recommend the Proof Setup command (View > Proof Setup -> Custom). This command lets you select the "proof profile" in the source space when printing. You can also see a simulation on your monitor. We recommend as follows: ENWW Get accurate colors from Adobe InDesign CS 77