Netgear FVS338 FVS338 Reference Manual - Page 51
Static Route Example, Destination IP Address, IP Subnet Mask, Interface, Gateway IP Address, Metric - static ip
 |
UPC - 606449037197
View all Netgear FVS338 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 51 highlights
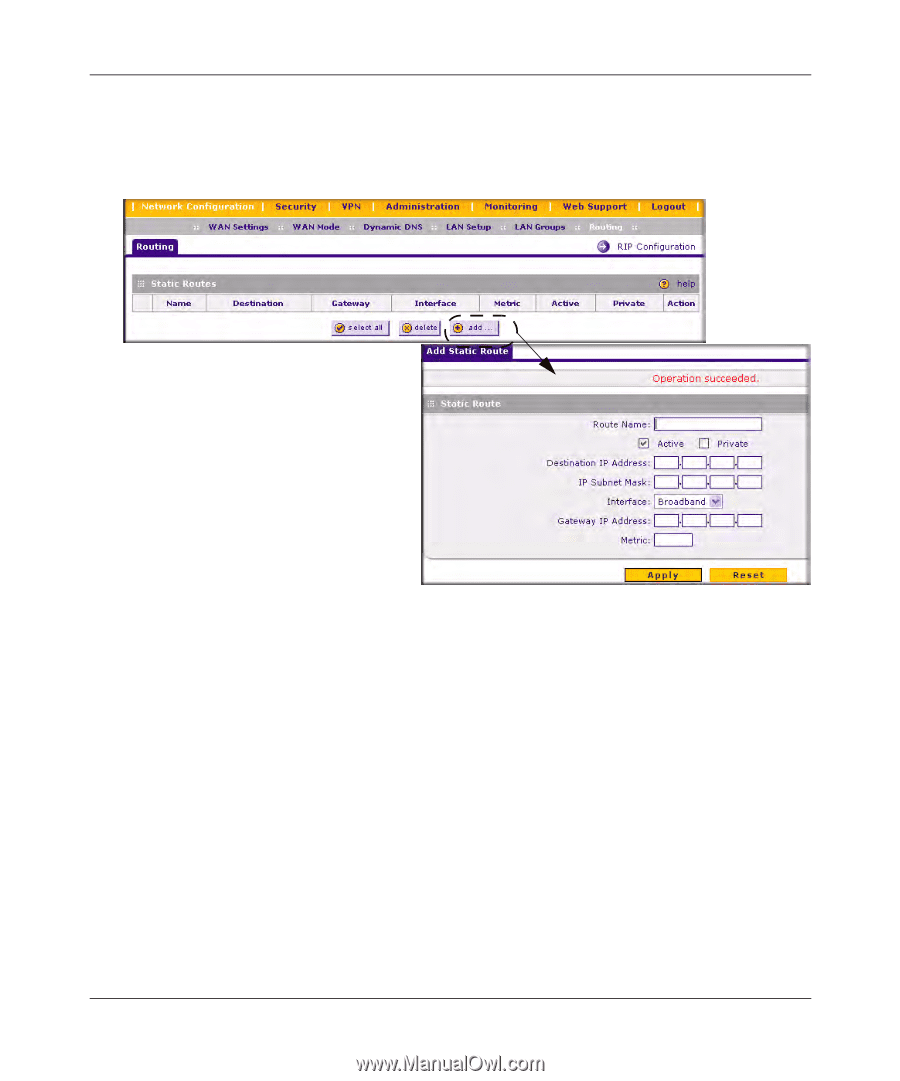
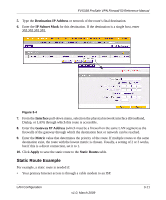
FVS338 ProSafe VPN Firewall 50 Reference Manual 5. Type the Destination IP Address or network of the route's final destination. 6. Enter the IP Subnet Mask for this destination. If the destination is a single host, enter 255.255.255.255. Figure 3-4 7. From the Interface pull-down menu, selection the physical network interface (Broadband, Dialup, or LAN) through which this route is accessible. 8. Enter the Gateway IP Address (which must be a firewall on the same LAN segment as the firewall) of the gateway through which the destination host or network can be reached. 9. Enter the Metric value that determines the priority of the route. If multiple routes to the same destination exist, the route with the lowest metric is chosen. Usually, a setting of 2 or 3 works, but if this is a direct connection, set it to 1. 10. Click Apply to save the static route to the Static Routes table. Static Route Example For example, a static route is needed if: • Your primary Internet access is through a cable modem to an ISP. LAN Configuration v1.0, March 2009 3-11