Sony HVR Z1U Operating Instructions - Page 116
Compatibility of the DVCAM and DV formats
 |
UPC - 027242668799
View all Sony HVR Z1U manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 116 highlights
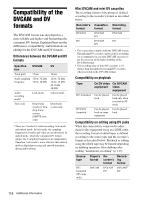
Compatibility of the DVCAM and DV formats The DVCAM format was developed as a more reliable and higher-end format than the consumer DV format. Explained here are the differences, compatibility, and limitations on editing for the DVCAM and DV formats. Differences between the DVCAM and DV formats Specifica- DVCAM DV tion Track pitch 15 µm 10 µm Audio sampling 12 bit: 32 kHz frequency 16 bit: 48 kHz 12 bit: 32 kHz 16 bit: 32 kHz, 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz Audio recording mode* Lock mode Unlock mode Time code Drop frame system or Nondrop frame system (SMPTE time code) Drop frame system only * There are 2 modes for audio recording, lock mode and unlock mode. In lock mode, the sampling frequencies of audio and video are synchronized. In unlock mode, which the consumer DV format adopts, the 2 sampling frequencies are independent. Therefore, lock mode is more effective than unlock mode in digital processing and smooth transition during audio editing. Mini DVCAM and mini DV cassettes The recording format of the picture is defined according to the recorder's format as described below. Recorder's Cassette's Recording format format format DVCAM DV DVCAM DV DVCAM DV DVCAM DV • This camcorder complies with the DVCAM format. Though mini DV cassettes can be used for recording, we recommend you use mini DVCAM cassettes to get the most out of the high reliability of the DVCAM format. • The recording time of mini DV cassettes is 1/3 shorter than that indicated on mini DV cassettes when recorded in the DVCAM format. Compatibility on playback Tape DV-formatted DVCAMformatted On DV video On DVCAM equipment video equipment Can be played back Can be played back only when recorded in SP mode Can be played back on some equipment Can be played back Compatibility on editing using DV jacks When this camcorder is connected to other digital video equipment using an i.LINK cable, the recording format of edited tapes is defined according to the source tape and the recorder's format as described below. Playback or editing using the edited tape may be limited depending on dubbing operation. Start dubbing after reading "Limitations on editing" (p. 117). Source tape DVformatted (SP mode only) Player's format DVCAM Recorder's format DVCAM DV Recording format DVCAM1) DV 116 Additional Information