Symantec BRIGHTMAIL Installation Guide - Page 15
Content Filters, Blocked and Allowed Senders Lists, Define a custom Allowed Senders List - blacklist
 |
UPC - 037648248754
View all Symantec BRIGHTMAIL manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 15 highlights
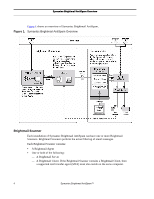
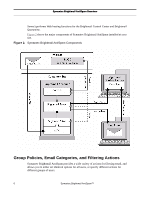
Symantec Brightmail AntiSpam Overview Signature Filters - When messages flow into the BLOC, they are characterized using proprietary algorithms into a unique signature, which is added to the database of known spam. Using this signature, Signature Filters group and match seemingly random messages that originated from a single attack. By distilling a complex and evolving attack to its DNA, more spam can be deflected with a single filter. Signature Filters include BrightSig2 Filters, Body Hash Filters and Attachment Filters. Header Filters - Header Filters are regular expression-based filters that are applied to the header lines of a message. Header Filters can be used to compare email messages to spam messages seen by the Probe Network, and to exploit commonalities or trends present in spam messages (similar to the use of Symantec's Heuristic Filters). Content Filters You can create custom content filters, using either the Custom Filters Editor provided through the Brightmail Control Center, or using a Sieve filters file. You can specify a wide variety of filtering criteria. You have three sets of choices for the action to take on these messages: • Deliver normally. • Treat the same as another email category: you can use the same action on custom- filtered messages that you chose for spam, viruses, or any other category. • Treat as company-specific content: choose a unique action for custom-filtered messages. Blocked and Allowed Senders Lists You can use lists of blocked and allowed senders (also known as blacklists and whitelists) in a variety of ways: • Define a custom Allowed Senders List - Allowed senders are approved or trusted senders. Unless AntiVirus Filters detect a virus or worm, Symantec Brightmail AntiSpam treats mail coming from an address or connection in your Allowed Senders List as legitimate mail. Such mail is delivered immediately to the inbox, bypassing any other filtering. You therefore cannot choose message handling actions for messages from allowed senders; by definition these messages will be delivered to the user inbox. • Define a custom Blocked Senders List - You can block messages from any senders you wish. You can define message handling actions that apply to messages from blocked senders for each group policy. • Check incoming mail against third party blocked senders lists and third party allowed senders lists - Third parties compile and manage lists of desirable or undesirable domains, IP connections, and networks. A DNS blacklist is a common example of such a list. DNS blacklists allow subscribers to check, using DNS lookups, whether incoming mail is originating from known spammers. Many of the hosts on the list typically are running open SMTP relays or open proxy server ports. Such insecure relays and ports are effective conduits for sending unsolicited bulk email. Subscribers Installation Guide 9