Sharp DX-B350P DX-B350P DX-B450P Operation Manual - Page 83
Networking, Protocols, Initial Setting of the Printer’s IP Address
 |
View all Sharp DX-B350P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 83 highlights
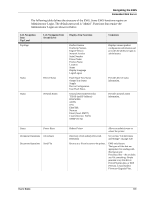
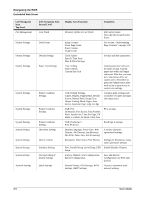
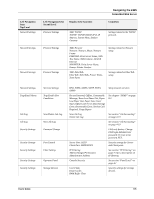
Chapter 7: Networking Protocols The DX-B350P/B450P is a fast network capable printer and supports an Ethernet 10/100 Base-Tx network connection. The following protocols are supported: TCP/IPv4, UDP, BOOTP, DHCP, ARP, ICMP, DDNS, WINS, LPR HTTP for Embedded Web Server IPv6, ICMPv6, Address Auto Configuration and Neighbor Discovery for IPv6 Host Resources MIB (RFC 1514), MIB II (RFC 1213), Printer MIBv2 (3805), SNMPv1/v2 Email SMTP client for alerts, POP3 for receiving print data Apple EtherTalk, Bonjour Netware V5.5, V6.5 IPX (SPX/NCP) LPD In this Chapter... • Protocols • Initial Setting of the Printer's IP Address • Configuring the Driver • Printer Network Configuration • Notifications • IP Filtering • IPv6 Implementation • SNMP Initial Setting of the Printer's IP Address All devices on the network must have an IP address. The printer comes configured from the factory to obtain an address automatically from your network's DHCP server. If your network does not support DHCP or you want to set the printer to a specific IP address, you must set it manually. Setting the IP Address through DHCP Many networks have a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server. A DHCP server automatically programs an IP address into every terminal and printer on the network that is configured to use DHCP. A DHCP server is built into most cable and DSL routers. If you use a cable or DSL router, see your the device documentation for information on IP addressing. 7-1