Yamaha Tyros4 Reference Manual - Page 52
HIGH KEY / NOTE LIMIT, RTR Retrigger Rule
 |
UPC - 086792947280
View all Yamaha Tyros4 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 52 highlights
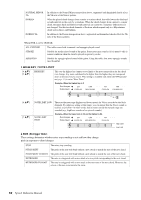
NATURAL MINOR 5th DORIAN DORIAN 5th In addition to the Natural Minor transposition above, augmented and diminished chords affect the 5th note of the Source pattern. When the played chord changes from a major to a minor chord, this table lowers the third and seventh intervals in the scale by a semitone. When the chord changes from a minor to a major chord, the minor third and flatted seventh intervals are raised by a semitone. Other notes are not changed. Use this for chord channels of Sections which respond only to a Major/minor chord such as Intros and Endings. In addition to the Dorian transposition above, augmented and diminished chords affect the 5th note of the Source pattern. When NTR is set to GUITAR ALL-PURPOSE This table covers both strummed- and arpeggio-played sound. STROKE Suitable for stroke-played sound of the guitar. Some notes may sound as if it is muted-this is normal condition when the chord is played on guitar by stroke. ARPEGGIO Suitable for arpeggio-played sound of the guitar. Using this table, four notes arpeggio sounds most beautiful. 3 HIGH KEY / NOTE LIMIT [4 ]/ [5 ] HIGH KEY This sets the highest key (upper octave limit) of the note transposition for the chord root change. Any notes calculated to be higher than the highest key are transposed down to the next lowest octave. This setting is available only when the NTR parameter (page 51) is set to "Root Trans." Example-When the highest key is F. Root changes Notes played CM C3-E3-G3 C#M C#3-E#3-G#3 FM F3-A3-C4 F#M F#2-A#2-C#3 [6 ] [7 ] NOTE LIMIT LOW NOTE LIMIT HIGH These set the note range (highest and lowest notes) for Voices recorded to the Style channels. By judicious setting of this range, you can ensure that the Voices sound as realistic as possible-in other words, that no notes outside the natural range are sounded (e.g., high bass sounds or low piccolo sounds). Example-When the lowest note is C3 and the highest is D4. Root changes Notes played CM E3-G3-C4 C#M E#3-G#3-C#4 FM F3-A3-C4 High Limit Low Limit 4 RTR (Retrigger Rule) These settings determine whether notes stop sounding or not and how they change pitch in response to chord changes. STOP The notes stop sounding. PITCH SHIFT The pitch of the note will bend without a new attack to match the type of the new chord. PITCH SHIFT TO ROOT The pitch of the note will bend without a new attack to match the root of the new chord. RETRIGGER The note is retriggered with a new attack at a new pitch corresponding to the next chord. RETRIGGER TO ROOT The note is retriggered with a new attack at the root note of the next chord. However, the octave of the new note remains the same. 52 Tyros4 Reference Manual