ZyXEL NBG334W User Guide - Page 143
Bandwidth Management
 |
View all ZyXEL NBG334W manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 143 highlights
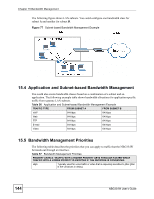
CHAPTER 15 Bandwidth Management This chapter contains information about configuring bandwidth management, editing rules and viewing the NBG334W's bandwidth management logs. 15.1 Bandwidth Management Overview ZyXEL's Bandwidth Management allows you to specify bandwidth management rules based on an application and/or subnet. You can allocate specific amounts of bandwidth capacity (bandwidth budgets) to different bandwidth rules. The NBG334W applies bandwidth management to traffic that it forwards out through an interface. The NBG334W does not control the bandwidth of traffic that comes into an interface. Bandwidth management applies to all traffic flowing out of the router, regardless of the traffic's source. Traffic redirect or IP alias may cause LAN-to-LAN traffic to pass through the NBG334W and be managed by bandwidth management. • The sum of the bandwidth allotments that apply to the WAN interface (LAN to WAN, WLAN to WAN, WAN to WAN / NBG334W) must be less than or equal to the Upstream Bandwidth that you configure in the Bandwidth Management Advanced screen. • The sum of the bandwidth allotments that apply to the LAN port (WAN to LAN, WLAN to LAN, LAN to LAN / NBG334W) must be less than or equal to 100,000 kbps (you cannot configure the bandwidth budget for the LAN port). • The sum of the bandwidth allotments that apply to the WLAN port (LAN to WLAN, WAN to WLAN, WLAN to WLAN / NBG334W) must be less than or equal to 54,000 kbps (you cannot configure the bandwidth budget for the WLAN port). 15.2 Application-based Bandwidth Management You can create bandwidth classes based on individual applications (like VoIP, Web, FTP, Email and Video for example). 15.3 Subnet-based Bandwidth Management You can create bandwidth classes based on subnets. NBG334W User's Guide 143