Dell PowerConnect J-SRX240 Hardware Guide - Page 83
Table 27: Port Settings When Connecting the Services Gateway to the CLI Locally
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect J-SRX240 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 83 highlights
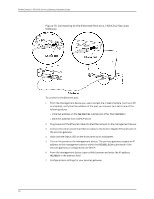
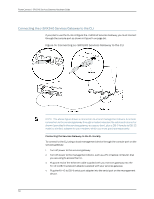
Chapter 13: Connecting the J-SRX240 Services Gateway to Management Devices 5. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the console port on the services gateway. 6. Turn on the power to the management device. 7. Start your asynchronous terminal emulation application (such as Microsoft Windows HyperTerminal) and select the appropriate COM port to use (for example, COM1). 8. Configure the port settings shown in Table 27 on page 67. Table 27: Port Settings When Connecting the Services Gateway to the CLI Locally Port Settings Value Bits per second 9600 Data bits 8 Parity None Stop bits 1 Flow control None 9. Power on the services gateway by pressing the Power button on the front panel. Verify that the Power LED on the front panel turns green. The terminal emulation screen on your management device displays the startup sequence. When the services gateway has finished starting up, a login prompt appears. 10. Log in as the user root. No password is required at initial connection, but you must assign a root password before committing any configuration settings. Connecting a Services Gateway to the CLI Remotely You can connect the services gateway to the CLI from a remote location through two dial-up modems: • A modem that is connected to the console port on the services gateway • A second modem connected to a remote management device The modem connection allows you to remotely perform the same console operations you can perform locally. Related Topics • Connecting the J-SRX240 Services Gateway to the J-Web Interface on page 63 • Connecting to the CLI at the User End for the J-SRX240 Services Gateway on page 69 • Connecting the Modem at the J-SRX240 Services Gateway End on page 68 • Connecting the Modem to the Console Port on the J-SRX240 Services Gateway on page 69 67