ZyXEL P-870MH-C1 User Guide - Page 138
Encryption, WPA-PSK, Table 39
 |
View all ZyXEL P-870MH-C1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 138 highlights
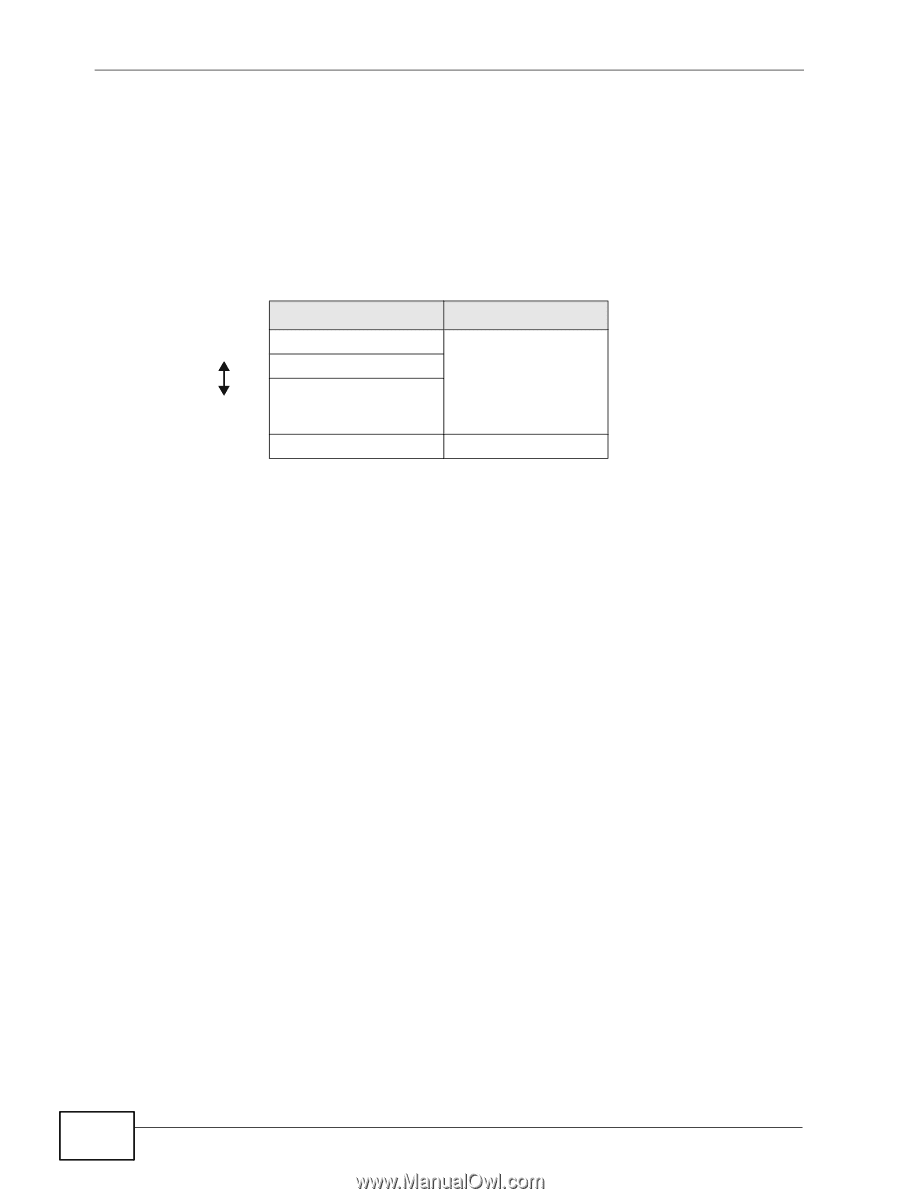
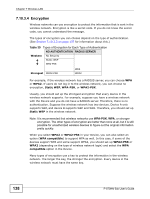
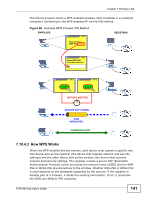
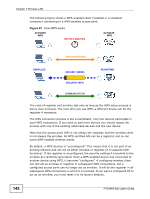
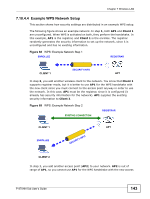
Chapter 7 Wireless LAN 7.10.3.4 Encryption Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the information that is sent in the wireless network. Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret code, you cannot understand the message. The types of encryption you can choose depend on the type of authentication. (See Section 7.10.3.3 on page 137 for information about this.) Table 39 Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication NO AUTHENTICATION RADIUS SERVER Weakest No Security Static WEP WPA-PSK Strongest WPA2-PSK WPA WPA2 For example, if the wireless network has a RADIUS server, you can choose WPA or WPA2. If users do not log in to the wireless network, you can choose no encryption, Static WEP, WPA-PSK, or WPA2-PSK. Usually, you should set up the strongest encryption that every device in the wireless network supports. For example, suppose you have a wireless network with the Device and you do not have a RADIUS server. Therefore, there is no authentication. Suppose the wireless network has two devices. Device A only supports WEP, and device B supports WEP and WPA. Therefore, you should set up Static WEP in the wireless network. Note: It is recommended that wireless networks use WPA-PSK, WPA, or stronger encryption. The other types of encryption are better than none at all, but it is still possible for unauthorized wireless devices to figure out the original information pretty quickly. When you select WPA2 or WPA2-PSK in your Device, you can also select an option (WPA compatible) to support WPA as well. In this case, if some of the devices support WPA and some support WPA2, you should set up WPA2-PSK or WPA2 (depending on the type of wireless network login) and select the WPA compatible option in the Device. Many types of encryption use a key to protect the information in the wireless network. The longer the key, the stronger the encryption. Every device in the wireless network must have the same key. 138 P-870HN-5xb User's Guide