ZyXEL P-870MH-C1 User Guide - Page 98
IP Address Assignment, Full Cone NAT
 |
View all ZyXEL P-870MH-C1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
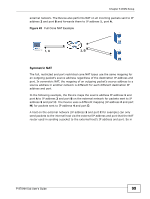
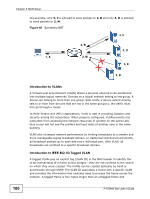
Chapter 5 WAN Setup Variable Bit Rate (VBR) The Variable Bit Rate (VBR) ATM traffic class is used with bursty connections. Connections that use the Variable Bit Rate (VBR) traffic class can be grouped into real time (VBR-RT) or non-real time (VBR-nRT) connections. The VBR-RT (real-time Variable Bit Rate) type is used with bursty connections that require closely controlled delay and delay variation. It also provides a fixed amount of bandwidth (a PCR is specified) but is only available when data is being sent. An example of an VBR-RT connection would be video conferencing. Video conferencing requires real-time data transfers and the bandwidth requirement varies in proportion to the video image's changing dynamics. The VBR-nRT (non real-time Variable Bit Rate) type is used with bursty connections that do not require closely controlled delay and delay variation. It is commonly used for "bursty" traffic typical on LANs. PCR and MBS define the burst levels, SCR defines the minimum level. An example of an VBR-nRT connection would be non-time sensitive data file transfers. Unspecified Bit Rate (UBR) The Unspecified Bit Rate (UBR) ATM traffic class is for bursty data transfers. However, UBR doesn't guarantee any bandwidth and only delivers traffic when the network has spare bandwidth. An example application is background file transfer. IP Address Assignment A static IP is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A dynamic IP is not fixed; the ISP assigns you a different one each time. The Single User Account feature can be enabled or disabled if you have either a dynamic or static IP. However the encapsulation method assigned influences your choices for IP address and default gateway. Full Cone NAT In full cone NAT, the NAT router maps all outgoing packets from an internal IP address and port to a single IP address and port on the external network. The NAT router also maps packets coming to that external IP address and port to the internal IP address and port. In the following example, the Device maps the source address of all packets sent from the internal IP address 1 and port A to IP address 2 and port B on the 98 P-870HN-5xb User's Guide