ZyXEL P-870MH-C1 User Guide - Page 69
Status > xDSL Statistics continued, Refresh Interval
 |
View all ZyXEL P-870MH-C1 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 69 highlights
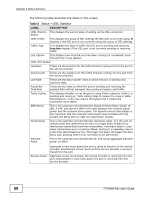
Chapter 4 Status Screens Table 8 Status > xDSL Statistics (continued) LABEL DESCRIPTION Actual INP Sudden spikes in the line's level of external noise (impulse noise) can cause errors and result in lost packets. This could especially impact the quality of multimedia traffic such as voice or video. Impulse noise protection (INP) provides a buffer to allow for correction of errors caused by error correction to deal with this. The number of DMT (Discrete MultiTone) symbols shows the level of impulse noise protection for the upstream and downstream traffic. A higher symbol value provides higher error correction capability, but it causes overhead and higher delay which may increase error rates in received multimedia data. Total Attenuation This is the upstream and downstream line attenuation, measured in decibels (dB). This attenuation is the difference between the power transmitted at the near-end and the power received at the far-end. Attenuation is affected by the channel characteristics (wire gauge, quality, condition and length of the physical line). Attainable Net Data Rate These are the highest theoretically possible transfer rates at which the port could send and receive payload data without transport layer protocol headers and traffic. xDSL Counters Downstream These are the statistics for the traffic direction coming into the port from the service provider. Upstream These are the statistics for the traffic direction going out from the port to the service provider. FEC This is the number of Far End Corrected blocks. CRC This is the number of Cyclic Redundancy Checks. ES This is the number of Errored Seconds meaning the number of seconds containing at least one errored block or at least one defect. SES This is the number of Severely Errored Seconds meaning the number of seconds containing 30% or more errored blocks or at least one defect. This is a subset of ES. UAS This is the number of UnAvailable Seconds. LOS This is the number of Loss Of Signal seconds. LOF This is the number of Loss Of Frame seconds. LOM This is the number of Loss of Margin seconds. Refresh Interval Enter the time interval for refreshing statistics in this field. Set Interval Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Refresh Interval field. Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics. P-870HN-5xb User's Guide 69