Dell PowerConnect 2848 User's Guide - Page 89
Manually Allocating IP Addresses (Static Hosts), Domain Name Server
 |
View all Dell PowerConnect 2848 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 89 highlights
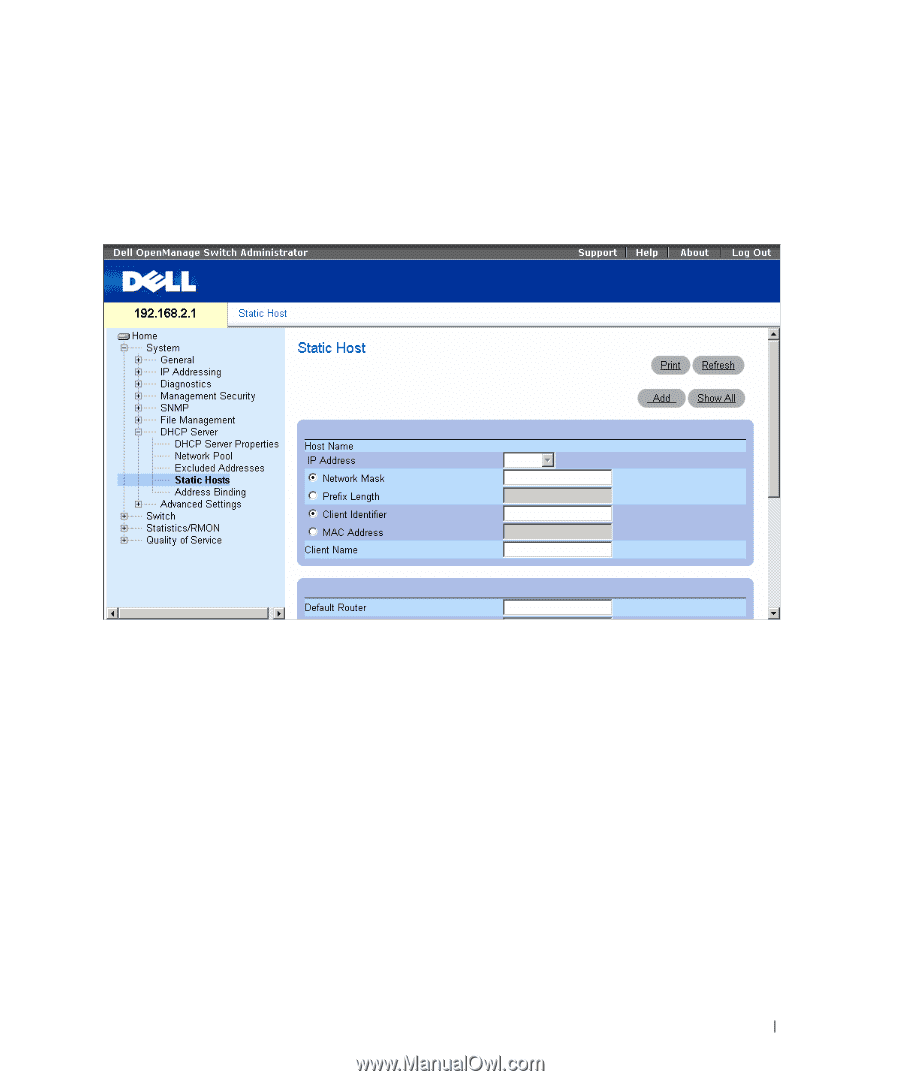
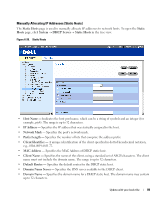
Manually Allocating IP Addresses (Static Hosts) The Static Hosts page is used to manually allocate IP addresses to network hosts. To open the Static Hosts page, click System → DHCP Server → Static Hosts in the tree view. Figure 6-28. Static Hosts • Host Name - Indicates the host pool name, which can be a string of symbols and an integer (for example, piy4). The range is up to 32 characters. • IP Address - Specifies the IP address that was statically assigned to the host. • Network Mask - Specifies the pool's network mask. • Prefix Length - Specifies the number of bits that comprise the address prefix. • Client Identifier - A unique identification of the client specified in dotted hexadecimal notation, e.g., 01b6.0819.6811.72. • MAC Address - Specifies the MAC Address of DHCP static host. • Client Name - Specifies the name of the client, using a standard set of ASCII characters. The client name must not include the domain name. The range is up to 32 characters. • Default Router - Specifies the default router for the DHCP static host. • Domain Name Server - Specifies the DNS server available to the DHCP client. • Domain Name - Specifies the domain name for a DHCP static host. The domain name may contain up to 32 characters. Update with your book title 89