HP StorageWorks 2/16V Brocade Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide - Supporting - Page 30
Specifying a time base, Fabric Watch does
 |
View all HP StorageWorks 2/16V manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 30 highlights
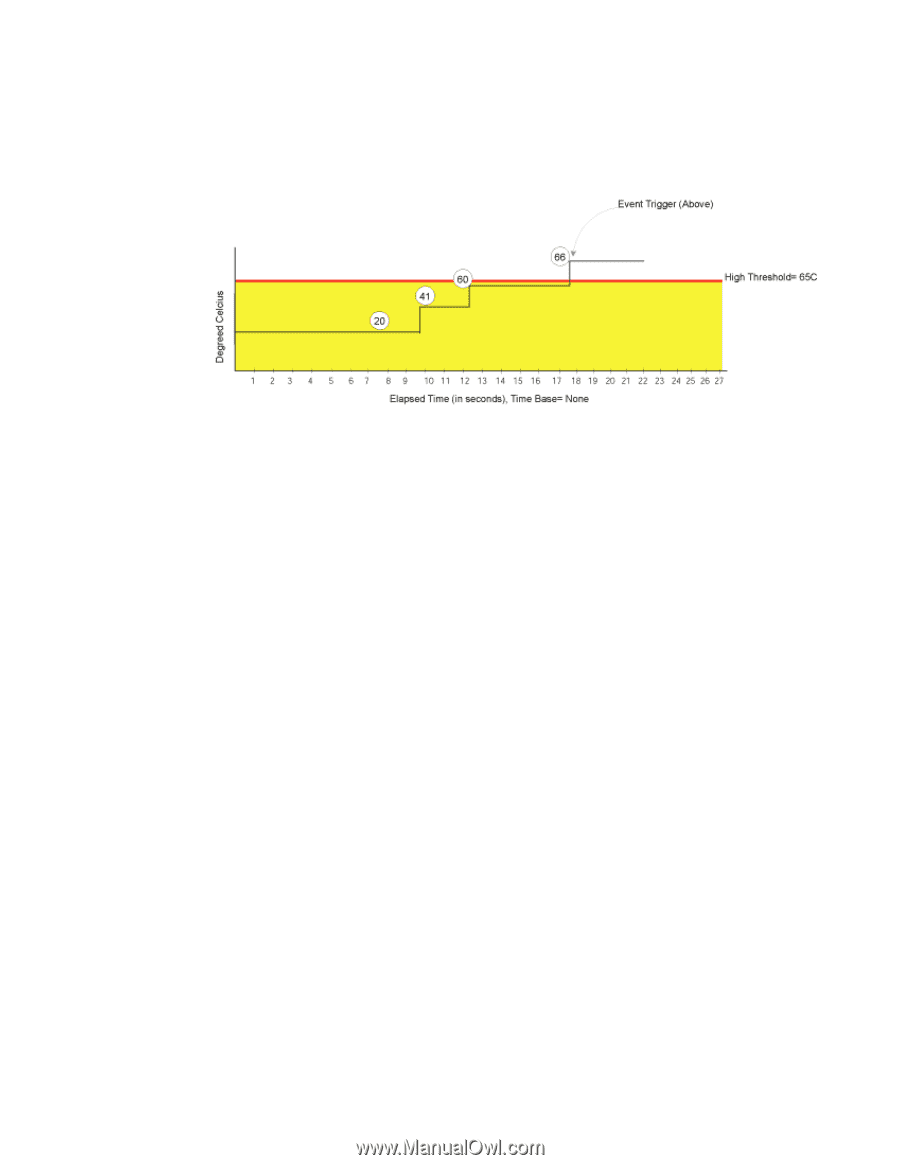
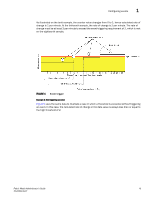
1 Configuring events Figure 3 shows a high limit of 65 degrees Celsius placed on a counter measuring temperature. During each sample period, Fabric Watch measures the temperature and compares it against the high threshold. If the measured temperature exceeds the high threshold, it triggers an event. FIGURE 3 Time base set to none Specifying a time base If you specify a time base value other than none (seconds, minute, hour, or day), Fabric Watch does not use the current data value. Instead, it calculates the difference between the current data value and the data value as it existed one time base ago. It compares this difference to the threshold boundary limit. For example, if you specify the time base minute, Fabric Watch calculates the counter value difference between two samples a minute apart. It then compares the difference (current data value - data value one minute ago) against the preset threshold boundary. When you set a time base to a value other than none, there are two main points to remember when configuring events: - Fabric Watch triggers an event only if the difference in the data value exceeds the preset threshold boundary limit. - Even if the current data value exceeds the threshold, Fabric Watch does not trigger an event if the rate of change is below the threshold limit. The following examples illustrate each point. Example1: Triggering an event Figure 4 shows a sample graph of data obtained by Fabric Watch (the type of data is irrelevant to the example). A high threshold of 2 is specified to trigger an event. A time base of minute is defined. An event occurs only if the rate of change in the specific interval (one minute in this example) is across the threshold boundary. It should be either higher than the high threshold limit or lower than the low threshold limit. 14 Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide 53-0000438-01