Cisco SGE2000 Configuration Guide - Page 37
Physically Connected Links Parameter, Priority, On-Failure Mode Parameter, SCE 2000, Inline
 |
View all Cisco SGE2000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 37 highlights
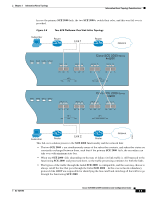
Chapter 3 Information About Topology Information About Topology Considerations • Single SCE 2000 inline installation = " Inline " connection mode. • Single SCE 2000 optical splitter installation = " Receive-only " connection mode. • Two SCE 2000 inline installation = " Inline-cascade " connection mode. • Two SCE 2000 optical splitter installation = " Receive-only-cascade " connection mode. Physically Connected Links Parameter If the system consists of more than one device, this parameter defines which link is connected to this SCE 2000 . Currently the system supports a maximum of two links, which are designated link 0 and link 1. Priority In a cascade topology, the user must define the priority of each SCE 2000 . • Primary - The Primary SCE 2000 is active by default • Secondary - The Secondary SCE 2000 is the default standby. Note that these defaults apply only when both devices are started together. However, if the primary SCE 2000 fails and then recovers, it will not revert to active status, but remains in standby status, while the secondary device remains active. On-Failure Mode Parameter As described in the section The Bypass Mechanism, the bypass card supports four different modes. The following two modes are possible when the SCE 2000 is not operational due to platform failure or boot: • Bypass - The optical splitter forwards traffic with no intervention of the control application running in the SCE 2000 platform, but monitoring functions continue uninterrupted. • Cutoff - There is no forwarding of traffic. The link is forced down, resulting in traffic cutoff at Layer1. The Forwarding mode enables control of traffic flow and is not compatible with the non-operational status. In a single SCE 2000 topology, the value of this parameter is determined by whether or not the link can be completely cut when the SCE 2000 fails, or whether traffic flow should continue across the link in spite of platform failure. • Cutoff mode is required for the following: - Redundant inline topology. - Non-redundant inline topology if value-added services are crucial and are more important than maintaining connectivity. • Bypass mode is required for the following: - Non-redundant inline topology if connectivity is crucial. OL-7824-06 Cisco SCE 2000 4xGBE Installation and Configuration Guide 3-11