D-Link DWC-1000 DWC-1000 User's Guide - Page 233
Appendix C. Glossary
 |
View all D-Link DWC-1000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 233 highlights
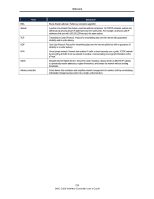
APPENDIX C. GLOSSARY Term Access point ARP CHAP DDNS DHCP DNS FQDN FTP HTTP IKE IPsec ISAKMP ISP MAC Address MTU NAT NetBIOS NTP PAP PPPoE PPTP RADIUS Definition A device that provides network access to wireless devices. Address Resolution Protocol. Broadcast protocol for mapping IP addresses to MAC addresses. Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol. Protocol for authenticating users to an ISP. Dynamic DNS. System for updating domain names in real time. Allows a domain name to be assigned to a device with a dynamic IP address. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Protocol for allocating IP addresses dynamically so that addresses can be reused when hosts no longer need them. Domain Name System. A hierarchical distributed naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. Fully qualified domain name. Complete domain name, including the host portion. Example: serverA.companyA.com. File Transfer Protocol. Protocol for transferring files between network nodes. Hypertext Transfer Protocol. Protocol used by web browsers and web servers to transfer files. Internet Key Exchange. Mode for securely exchanging encryption keys in ISAKMP as part of building a VPN tunnel. IP security. Suite of protocols for securing VPN tunnels by authenticating or encrypting IP packets in a data stream. IPsec operates in either transport mode (encrypts payload but not packet headers) or tunnel mode (encrypts both payload and packet headers). Internet Key Exchange Security Protocol. Protocol for establishing security associations and cryptographic keys on the Internet. Internet service provider. Media-access-control address. Unique physical-address identifier attached to a network adapter. Maximum transmission unit. Size, in bytes, of the largest packet that can be passed on. The MTU for Ethernet is a 1500-byte packet. Network Address Translation. Process of rewriting IP addresses as a packet passes through a controller or firewall. NAT enables multiple hosts on a LAN to access the Internet using the single public IP address of the LAN's gateway controller. Microsoft Windows protocol for file sharing, printer sharing, messaging, authentication, and name resolution. Network Time Protocol. Protocol for synchronizing a controller to a single clock on the network, known as the clock master. Password Authentication Protocol. Protocol for authenticating users to a remote access server or ISP. Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet. Protocol for connecting a network of hosts to an ISP without the ISP having to manage the allocation of IP addresses. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol. Protocol for creation of VPNs for the secure transfer of data from remote clients to private servers over the Internet. Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service. Protocol for remote user authentication and accounting. Provides centralized management of usernames and passwords. 233 DWC-1000 Wireless Controller User's Guide