Netgear WNDAP360 WNDAP360 Reference Manual - Page 93
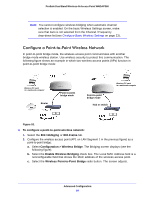
Con a Point-to-Multipoint Wireless Network
 |
View all Netgear WNDAP360 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
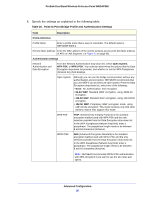
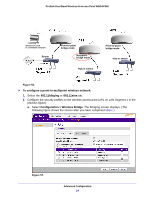
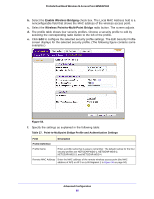
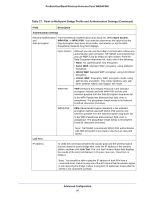
ProSafe Dual Band Wireless-N Access Point WNDAP360 Table 26. Point-to-Point Bridge Profile and Authentication Settings (Continued) Field Description Link Test IP Address To verify the connection between the access point and the wireless station that you intend to build a bridge with, enter the IP address of the wireless station, and then click Link Test. The Link Test Process Status field displays the results of the test (Uninitialized, In Process, Success, Timed Out, or Failure). Note: You should be able to ping the IP address of both APs from a connected client. Failure to ping one of the APs means that the wireless signal is not traversing the bridge. Failure to ping both IP addresses means that the clients is not connected correctly. g. Click Apply to save your security profile settings. The Bridging screen displays again. h. If the correct profile name and security option are displayed in the table, select the check box in the Enable column. i. Click Apply in the Bridging screen to save your point-to-point bridge settings. 3. Configure a second wireless access point (AP2) on LAN Segment 2 (see Figure 53 on page 90) in point-to-point bridge mode. AP1 needs to have AP2's MAC address in its Remote MAC Address field, and AP2 needs to have AP1's MAC address in its Remote MAC Address field. 4. Configure and verify the following settings for both wireless access points: • Verify the LAN network configuration of the wireless access points. Both need to be configured to operate in the same LAN network address range as the LAN devices. • Both wireless access points need to use the same channel, authentication mode, and security settings. 5. Verify connectivity across the LAN 1 and LAN 2. A computer on either LAN segment should be able to connect to the Internet or share files and printers of any other computers or servers connected to LAN Segment 1 or LAN Segment 2. Configure a Point-to-Multipoint Wireless Network In a point-to-multipoint bridge, the wireless access point is the master for a group of bridge-mode wireless access points. All traffic is sent to the master rather than to the other wireless access points. Use wireless security to protect this communication. For each wireless access point that you want the master to be able to connect to, you need to configure a security profile with a unique name and the MAC address of the wireless access point. You can configure up to four such security profiles (NETGEAR-WDS-1, NETGEAR-WDS-2, and so on). The following figure shows an example in which AP1 functions in point-to-multipoint bridge mode and AP2 and AP3 function in point-to-point bridge mode: Advanced Configuration 93