ZyXEL UAG715 User Guide - Page 140
PPPoE/PPTP Overview
 |
View all ZyXEL UAG715 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 140 highlights
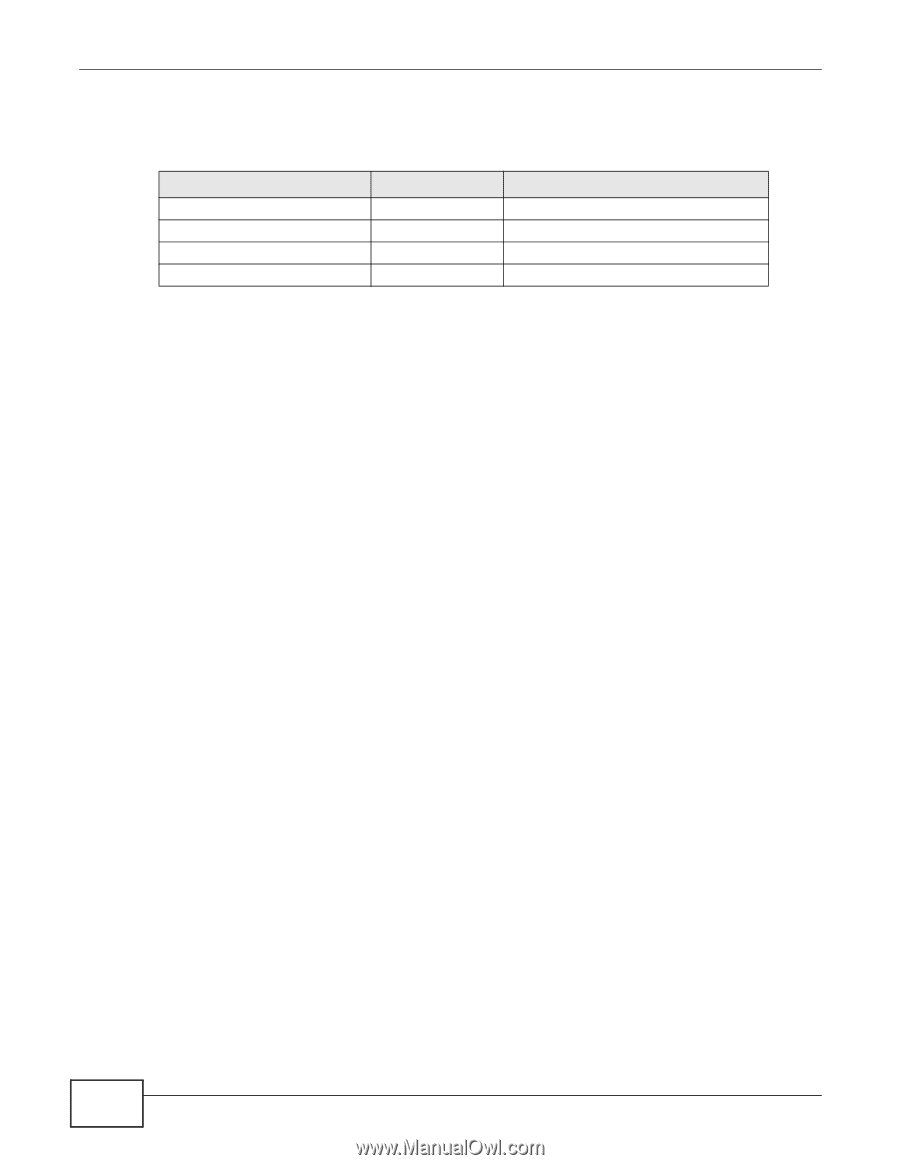
Chapter 8 Interfaces • IP address - If the DHCP client's MAC address is in the UAG's static DHCP table, the interface assigns the corresponding IP address. If not, the interface assigns IP addresses from a pool, defined by the starting address of the pool and the pool size. Table 55 Example: Assigning IP Addresses from a Pool START IP ADDRESS POOL SIZE RANGE OF ASSIGNED IP ADDRESS 50.50.50.33 5 50.50.50.33 - 50.50.50.37 75.75.75.1 200 75.75.75.1 - 75.75.75.200 99.99.1.1 1023 99.99.1.1 - 99.99.4.255 120.120.120.100 100 120.120.120.100 - 120.120.120.199 The UAG cannot assign the first address (network address) or the last address (broadcast address) in the subnet defined by the interface's IP address and subnet mask. For example, in the first entry, if the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, the UAG cannot assign 50.50.50.0 or 50.50.50.255. If the subnet mask is 255.255.0.0, the UAG cannot assign 50.50.0.0 or 50.50.255.255. Otherwise, it can assign every IP address in the range, except the interface's IP address. If you do not specify the starting address or the pool size, the interface the maximum range of IP addresses allowed by the interface's IP address and subnet mask. For example, if the interface's IP address is 9.9.9.1 and subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, the starting IP address in the pool is 9.9.9.2, and the pool size is 253. • Subnet mask - The interface provides the same subnet mask you specify for the interface. See IP Address Assignment on page 137. • Gateway - The interface provides the same gateway you specify for the interface. See IP Address Assignment on page 137. • DNS servers - The interface provides IP addresses for up to three DNS servers that provide DNS services for DHCP clients. You can specify each IP address manually (for example, a company's own DNS server), or you can refer to DNS servers that other interfaces received from DHCP servers (for example, a DNS server at an ISP). These other interfaces have to be DHCP clients. It is not possible for an interface to be the DHCP server and a DHCP client simultaneously. WINS WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) is a Windows implementation of NetBIOS Name Server (NBNS) on Windows. It keeps track of NetBIOS computer names. It stores a mapping table of your network's computer names and IP addresses. The table is dynamically updated for IP addresses assigned by DHCP. This helps reduce broadcast traffic since computers can query the server instead of broadcasting a request for a computer name's IP address. In this way WINS is similar to DNS, although WINS does not use a hierarchy (unlike DNS). A network can have more than one WINS server. Samba can also serve as a WINS server. PPPoE/PPTP Overview Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE, RFC 2516) and Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP, RFC 2637) are usually used to connect two computers over phone lines or broadband connections. PPPoE is often used with cable modems and DSL connections. It provides the following advantages: • The access and authentication method works with existing systems, including RADIUS. • You can access one of several network services. This makes it easier for the service provider to offer the service 140 UAG715 User's Guide