Dell Broadcom NetXtreme Family of Adapters Broadcom NetXtreme 57XX User Guide - Page 148
Driver Support by Operating System
 |
View all Dell Broadcom NetXtreme Family of Adapters manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 148 highlights
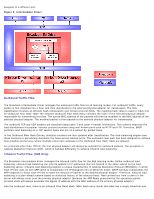
The following are the key attributes of Generic Static Trunking: Failover mechanism (link loss detection) Load balancing algorithm. Outbound traffic is balanced through Broadcom proprietary mechanism based L4 flows. Inbound traffic is balanced according to a switch specific mechanism. Outbound Load Balancing using MAC Address is not supported. Outbound Load Balancing using IP address is supported. Multivendor teaming is supported (must include at least one Broadcom Ethernet adapter as a team member) Applications Generic trunking works with switches that support Cisco Fast EtherChannel, Cisco Gigabit EtherChannel, Extreme Networks Load Sharing and Bay Networks or IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation static mode. Since load balancing is implemented on Layer 2 addresses, all higher protocols such as IP, IPX, and NetBEUI are supported. Therefore, this is the recommended teaming mode when the switch supports generic trunking modes over SLB. Configuration Recommendations Static trunking supports connecting the teamed ports to switches if they are on the same broadcast domain and support generic trunking. It does not support connecting to a router or Layer 3 switches since the ports must be on the same subnet. Dynamic Trunking (IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation) This mode supports link aggregation through static and dynamic configuration via the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP). With this mode, all adapters in the team are configured to receive packets for the same MAC address. The MAC address of the first adapter in the team is used and cannot be substituted for a different MAC address. The BASP driver determines the load-balancing scheme for outbound packets, using Layer 4 protocols previously discussed, whereas the team's link partner determines the load-balancing scheme for inbound packets. Because the load balancing is implemented on Layer 2, all higher protocols such as IP, IPX, and NetBEUI are supported. The attached switch must support the 802.3ad Link Aggregation standard for this mode of operation. The switch manages the inbound traffic to the adapter while the BASP manages the outbound traffic. Both the BASP and the switch continually monitor their ports for link loss. In the event of link loss on any port, traffic is automatically diverted to other ports in the team. Network Communications The following are the key attributes of Dynamic Trunking: Failover mechanism - Link loss detection Load Balancing Algorithm - Outbound traffic is balanced through a Broadcom proprietary mechanism based on L4 flows. Inbound traffic is balanced according to a switch specific mechanism. Outbound Load Balancing using MAC Address - No Outbound Load Balancing using IP Address - Yes Multivendor teaming - Supported (must include at least one Broadcom Ethernet adapter as a team member) Applications Dynamic trunking works with switches that support IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation dynamic mode using LACP. Inbound load balancing is switch dependent. In general, the switch traffic is load balanced based on L2 addresses. In this case, all network protocols such as IP, IPX, and NetBEUI are load balanced. Therefore, this is the recommended teaming mode when the switch supports LACP, except when switch fault tolerance is required. SLB is the only teaming mode that supports switch fault tolerance. Configuration Recommendations Dynamic trunking supports connecting the teamed ports to switches as long as they are on the same broadcast domain and supports IEEE 802.3ad LACP trunking. It does not support connecting to a router or Layer 3 switches since the ports must be on the same subnet. Driver Support by Operating System As previously noted, the BASP is supported in the Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, and NetWare operating system environments. In a NetWare environment, NESL support is required because BASP relies on the adapter drivers to