HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Security Configuration Guide - Page 19
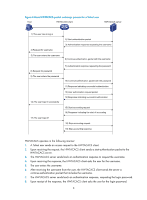
Basic LDAP packet exchange process,
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 19 highlights
1. An LDAP client uses the LDAP server administrator DN to bind with the LDAP server, establishes a connection to the server, and obtains the search rights. 2. The LDAP client uses the username in the authentication information of a user to construct search conditions, searches for the user in the specified root directory of the server, and obtains a user DN list. 3. The LDAP client uses each user DN in the obtained user DN list and the user's password to bind with the LDAP server. If a binding succeeds, the user is a legal user. The LDAP authorization process is similar to the LDAP authentication process. The difference is that the client gets the authorization information as well as the user DN list at step 2. If the authorization information satisfies the authorization need, the authorization process ends. Otherwise, the client uses the LDAP server administrator DN to bind with the LDAP server again, constructs search conditions by using the user DN list, and searches for other required authorization information. Basic LDAP packet exchange process The following example illustrates how the basic packet exchange process goes on during LDAP authentication and authorization for a Telnet user. Figure 7 Basic packet exchange process for LDAP authentication of a Telnet user Host LDAP client LDAP server 1) The user logs in by Telnet 10) The user logs in successfully 2) Establish a TCP connection 3) Administrator bind request 4) Bind response 5) User DN search request 6) Search response 7) User DN bind request 8) Bind response 9) Authorization The basic packet exchange process is as follows: 1. A Telnet user initiates a connection request and sends the username and password to the LDAP client. 2. Upon receiving the request, the LDAP client establishes a TCP connection with the LDAP server. 3. The LDAP client uses the administrator DN and password to send an administrator bind request to the LDAP server to obtain the search right. 4. The LDAP server processes the request. If the bind operation is successful, the LDAP server sends an acknowledgement to the LDAP client. 5. The LDAP client sends a user DN search request with the username of the Telnet user to the LDAP server. 10