HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Security Configuration Guide - Page 232
IKE security mechanism, Identity authentication, DH algorithm
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 232 highlights
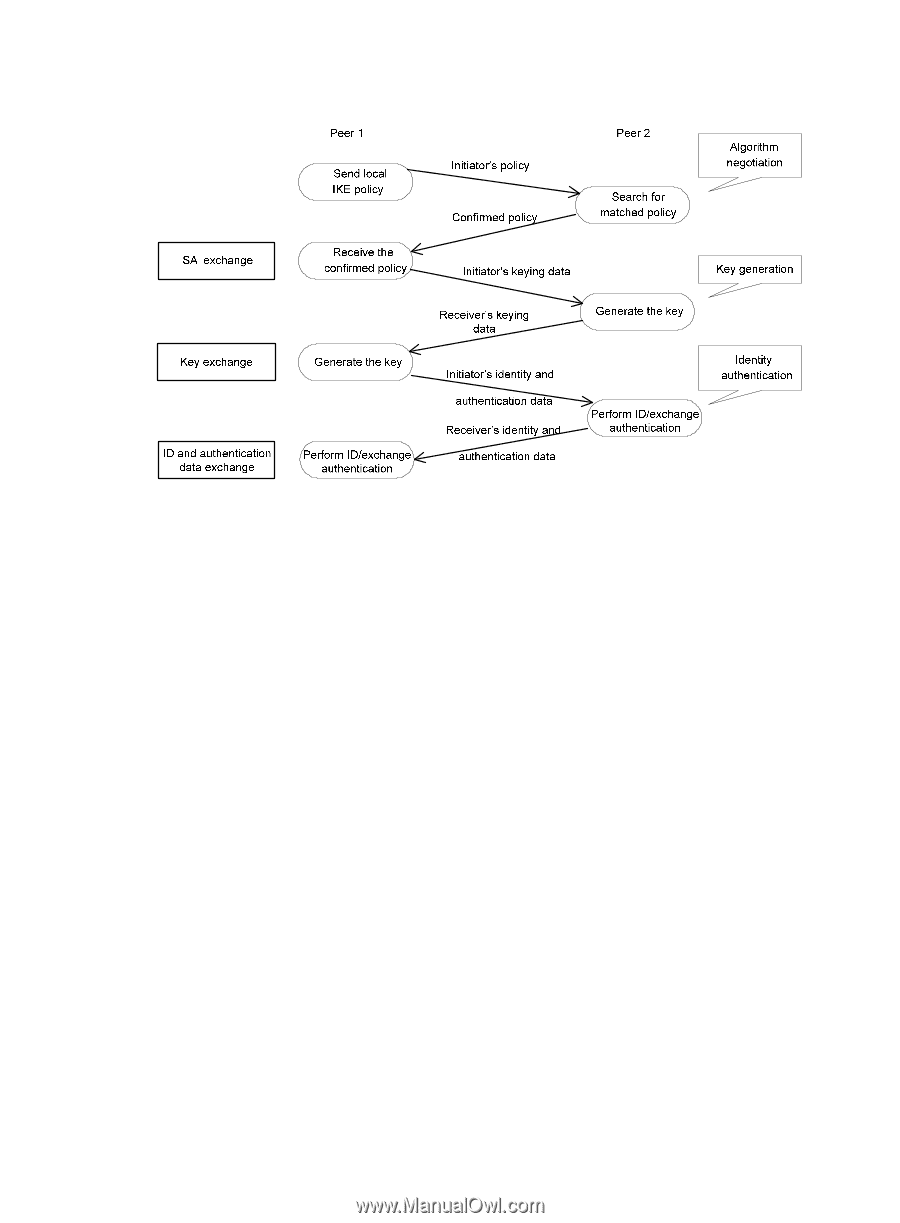
Figure 76 IKE exchange process in main mode As shown in Figure 76, the main mode of IKE negotiation in phase 1 involves three pairs of messages: • SA exchange-Used for negotiating the security policy. • Key exchange-Used for exchanging the DH public value and other values like the random number. The two peers use the exchanged data to generate key data and use the encryption key and authentication key to ensure the security of IP packets. • ID and authentication data exchange-Used for identity authentication. The main difference between the main mode and the aggressive mode is that the aggressive mode does not provide identity information protection and exchanges only three messages, rather than three pairs. The main mode provides identity information protection but is slower. IKE security mechanism IKE has a series of self-protection mechanisms and supports secure identity authentication, key distribution, and IPsec SA establishment on insecure networks. Identity authentication The IKE identity authentication mechanism is used to authenticate the identity of the communicating peers. The device supports Pre-shared key authentication-Two communicating peers use the pre-configured shared key for identity authentication. The pre-shared key authentication method does not require certificates and is easy to configure. It is usually deployed in small networks. DH algorithm The DH algorithm is a public key algorithm. With this algorithm, two peers can exchange keying material and then use the material to calculate the shared keys. Due to the decryption complexity, a third party cannot decrypt the keys even after intercepting all keying materials. 223