HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch Security Configuration Guide - Page 220
Applying an IPsec policy to an interface
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 220 highlights
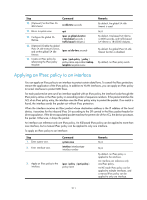
Step 10. (Optional.) Set the IPsec SA idle timeout. Command sa idle-time seconds 11. Return to system view. quit 12. Configure the global SA lifetime. ipsec sa global-duration { time-based seconds | traffic-based kilobytes } 13. (Optional.) Enable the global IPsec SA idle timeout function, and set the global SA idle timeout. ipsec sa idle-time seconds 14. Create an IPsec policy by referencing the IPsec policy template. ipsec { ipv6-policy | policy } policy-name seq-number isakmp template template-name Remarks By default, the global SA idle timeout is used. N/A By default, time-based SA lifetime is 3600 seconds, and traffic-based SA lifetime is 1843200 kilobytes. By default, the global IPsec SA idle timeout function is disabled. By default, no IPsec policy exists. Applying an IPsec policy to an interface You can apply an IPsec policy to an interface to protect certain data flows. To cancel the IPsec protection, remove the application of the IPsec policy. In addition to VLAN interfaces, you can apply an IPsec policy to tunnel interfaces to protect GRE flows. For each packet to be sent out of an interface applied with an IPsec policy, the interface looks through the IPsec policy entries in the IPsec policy in ascending order of sequence numbers. If the packet matches the ACL of an IPsec policy entry, the interface uses the IPsec policy entry to protect the packet. If no match is found, the interface sends the packet out without IPsec protection. When the interface receives an IPsec packet whose destination address is the IP address of the local device, it searches for the inbound IPsec SA according to the SPI carried in the IPsec packet header for de-encapsulation. If the de-encapsulated packet matches the permit rule of the ACL, the device processes the packet. Otherwise, it drops the packet. An interface can reference only one IPsec policy. An IKE-based IPsec policy can be applied to more than one interface, but a manual IPsec policy can be applied to only one interface. To apply an IPsec policy to an interface: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter interface view. Command system-view interface interface-type interface-number 3. Apply an IPsec policy to the interface. ipsec { policy | ipv6-policy } policy-name Remarks N/A N/A By default, no IPsec policy is applied to the interface. An interface can reference only one IPsec policy. An IKE-mode IPsec policy can be applied to multiple interfaces, and a manual IPsec policy can be applied to only one interface. 211