HP Dc5750 WebPAM User Manual - Page 105
Cache Settings, Migration and Expansion, Physical Drive Write Cache, Write Back Cache, Result
 |
UPC - 883585056446
View all HP Dc5750 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 105 highlights
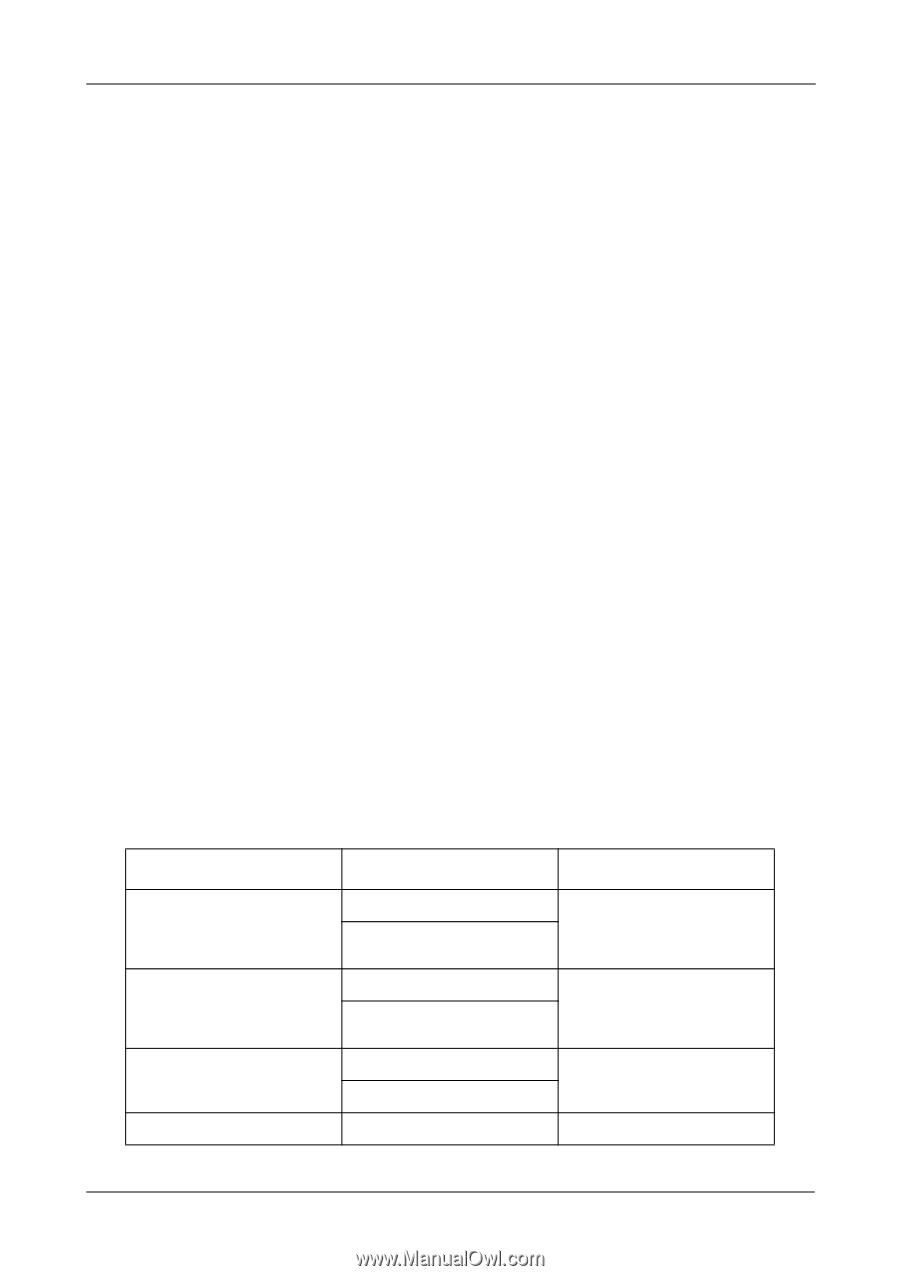
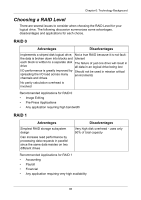
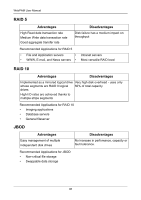
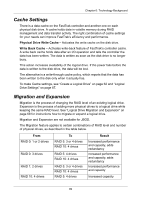
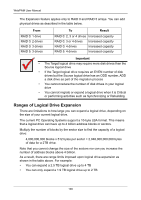
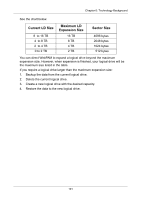
Chapter 6: Technology Background Cache Settings There is a data cache on the FastTrak controller and another one on each physical disk drive. A cache holds data in volatile memory during RAID management and data transfer activity. The right combination of cache settings for your needs can improve FastTrak's efficiency and performance. Physical Drive Write Cache - Activates the write cache on the disk drive. Write Back Cache - Activates write-back feature of FastTrak's controller cache. A write back cache holds data after an I/O operation and tells the controller the data has been written. The data is written as soon as the disk drive is no longer busy. This action increases availability of the logical drive. If the power fails before the data is written to the disk drive, the data will be lost. The alternative is a write-through cache policy, which reports that the data has been written to the disk only when it actually has. To make Cache settings, see "Create a Logical Drive" on page 62 and "Logical Drive Settings" on page 67. Migration and Expansion Migration is the process of changing the RAID level of an existing logical drive. Expansion is the process of adding more physical drives to a logical drive while keeping the same RAID level. See "Logical Drive Migration and Expansion" on page 68 for instructions how to migrate or expand a logical drive. Migration and Expansion are not available for JBOD. The Migration feature applies to certain combinations of RAID level and number of physical drives, as described in the table below. From RAID 0: 1 or 2 drives RAID 0: 3 drives RAID 1: 2 drives RAID 10: 4 drives To RAID 5: 3 or 4 drives RAID 10: 4 drives RAID 5: 4 drives RAID 10: 4 drives RAID 5: 3 or 4 drives RAID 10: 4 drives RAID 5: 4 drives Result Increased performance and capacity, adds redundancy ncreased performance and capacity, adds redundancy Increased performance and capacity Increased capacity 99