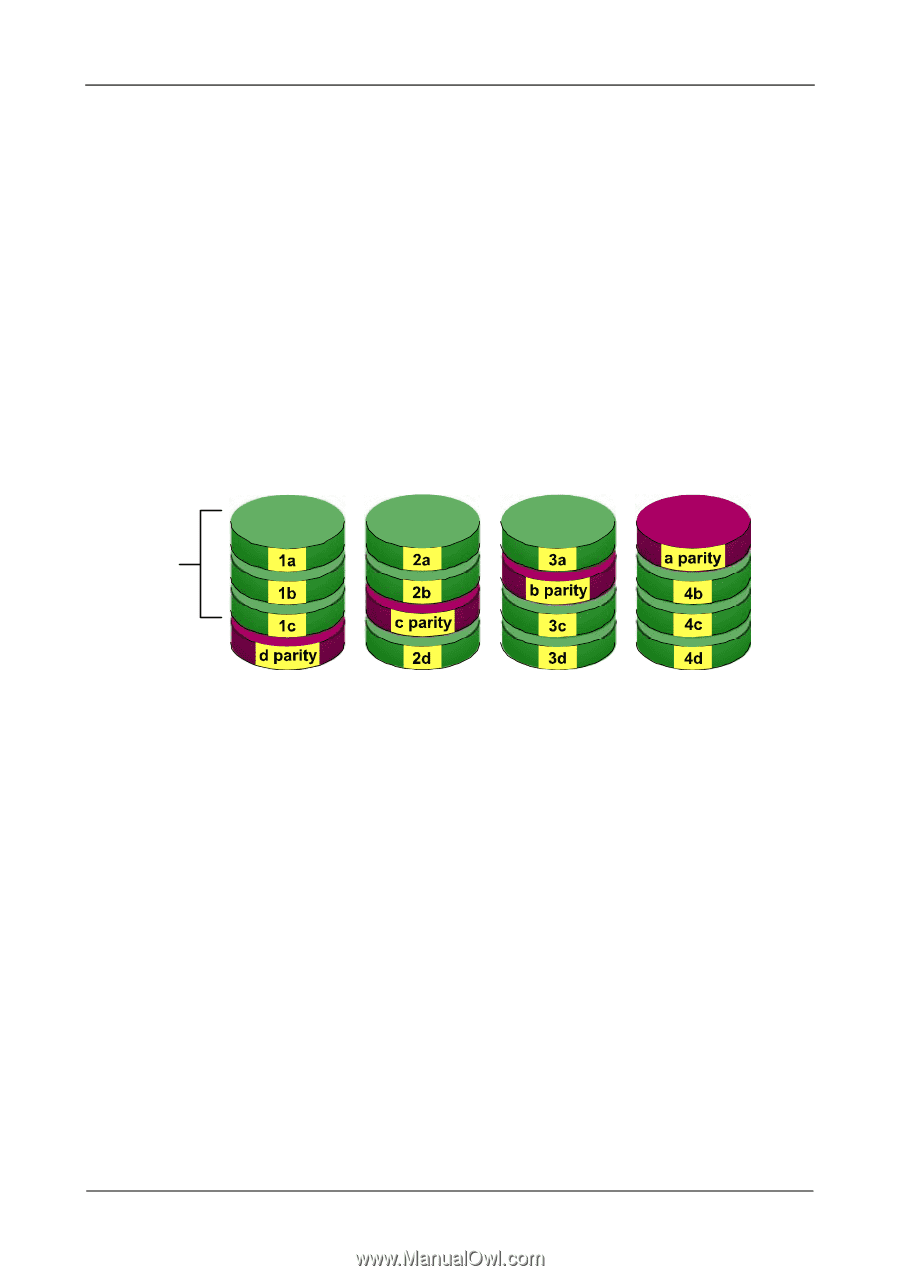HP Dc5750 WebPAM User Manual - Page 98
RAID 5 - Block Striping with Distributed Parity
 |
UPC - 883585056446
View all HP Dc5750 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 98 highlights
WebPAM User Manual RAID 5 - Block Striping with Distributed Parity RAID 5 organizes data across the disk drives of the logical drive, and stores parity information on to a disk drive dedicated to this purpose. This organization allows increased performance by accessing multiple disk drives simultaneously for each operation, as well as fault tolerance by providing parity data. In the event of a disk drive failure, data can be re-calculated by the RAID system based on the remaining data and the parity information. Parity data is distributed across the disk drives along with the data blocks. In each case, the parity data is stored on a different disk than its corresponding data block. RAID 5 makes efficient use of hard drives and is the most versatile RAID Level. It works well for file, database, application and web servers. Distributed Parity Data Blocks Disk Drives Figure 3. RAID 5 Stripes all drives with data and parity information The capacity of a RAID 5 logical drive is the smallest disk drive size multiplied by the number of disk drives, less one. Hence, a RAID 5 logical drive with four 100 GB disk drives will have a capacity of 300 GB. A logical drive with two 120 GB disk drives and one 100 GB disk drive will have a capacity of 200 GB. RAID 5 logical drives on FastTrak consist of 3 or 4 disk drives. 92